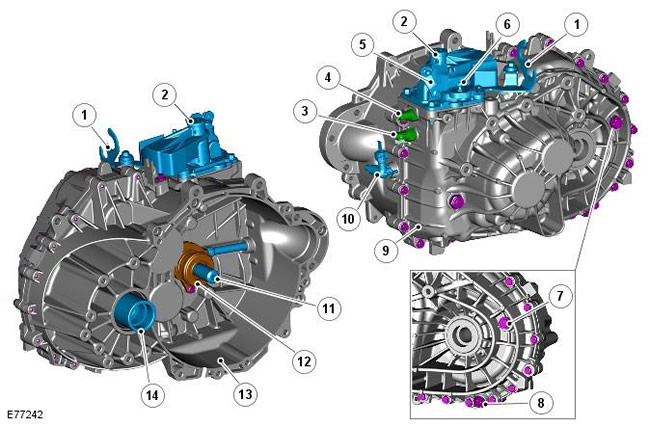
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | cable attachment bracket |
| 2 | - | trailing arm |
| 3 | - | 1st gear position switch |
| 4 | - | Reverse gear switch |
| 5 | - | Wishbone |
| 6 | - | Shift cable ball head |
| 7 | - | Transmission Fluid Level Plug/Filler Plug |
| 8 | - | Gearbox drain plug |
| 9 | - | gearbox housing |
| 10 | - | Clutch Hydraulic Air Release Adapter |
| 11 | - | input shaft |
| 12 | - | clutch slave cylinder |
| 13 | - | clutch housing |
| 14 | - | Differential output (right side shown). |
Neutral sensor
(vehicles with the system «Stop/Start» - from model year 2010)
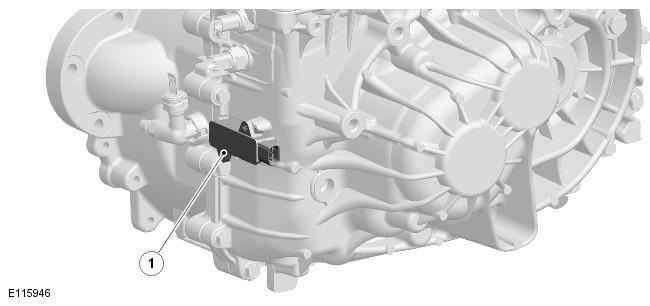
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Neutral sensor |
Magnetic-inductive PLCD-sensor installed on vehicles with the system «Stop/Start», is located outside the gearbox housing and is hard-wired to the engine control unit. The sensor is designed to determine the inclusion of a neutral gear within the calibrated window. For more information, see the chapter: Starting system (303-06C Starting system - 2.2L Duratorq - Td4, Vehicles built from 03/2009, Description and function).
Switch mechanism
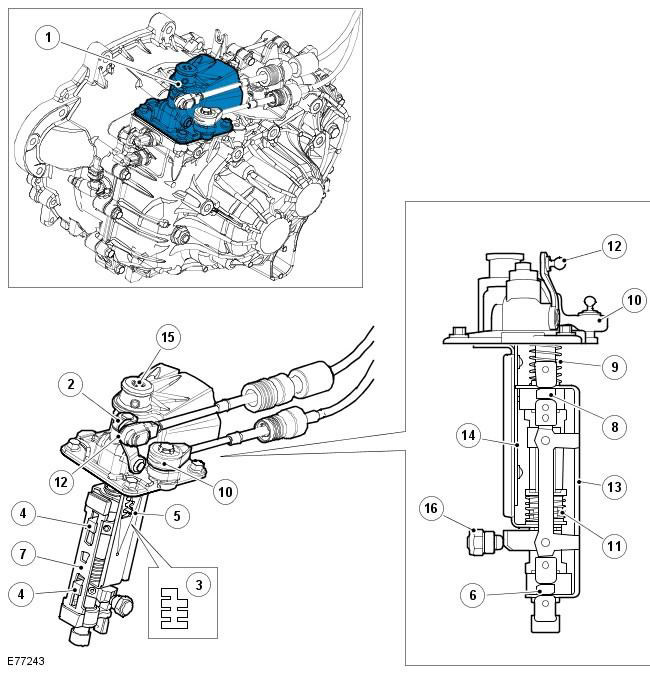
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Switch mechanism |
| 2 | - | Ball stop 5th - 6th gear |
| 3 | - | Gear shift gate |
| 4 | - | Flange |
| 5 | - | Gear shift finger |
| 6 | - | Lower Gear Selector |
| 7 | - | Selector rod |
| 8 | - | Upper gear selector |
| 9 | - | Spring |
| 10 | - | trailing arm |
| 11 | - | Spring |
| 12 | - | Wishbone |
| 13 | - | fixing plate |
| 14 | - | carrier plate |
| 15 | - | air release cap |
| 16 | - | Selector ball stop |
The gearbox is controlled by two shift cables connected to the selector lever. Selector lever movement is transmitted via cables to two linkages on top of the gearbox. The levers actuate the gearshift mechanism to select the requested gear ratio.
The shift mechanism is located at the front of the gearbox and transfers the movement of the shift cable to the shift actuators.
The shift mechanism is a one-piece block fixed to the gearbox housing with four bolts. The shift mechanism moves the upper and lower selector forks through the transverse and trailing arms at the top of the shift mechanism. There are two upper shift forks and two lower shift forks:
- The two upper shift forks are used to engage reverse gear, 1st and 2nd gears.
- The two lower shift forks are used to select 3rd, 4th, 5th and 6th gears.
The four shift forks transmit the movement from the shift mechanism to the corresponding synchronizer clutch. The shift forks are mounted in bearings in the gearbox housing.
Two carrier plates transmit torque from the trailing arm to the sliding shift selectors. The carrier plates are located and operate in a groove on the selector plate.
The carrier plates can be moved in a vertical plane between 4 positions. Different gears are selected from one of four positions as follows:
- Highest position - shift selector selects reverse gear
- Second up position - shift selector selects 1st and 2nd gears
- Second down position - shift selector selects 5th and 6th gears
- Lowest position - shift selector selects 3rd and 4th gears
The shift mechanism has two springs that return the selector lever to the neutral position.
Gear selector shafts
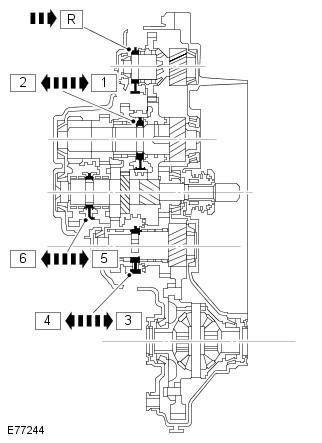
The illustration above shows the clutches for each group of gears. By moving these clutches in accordance with the choice of the shift mechanism, the required gears are connected to obtain the required gear ratio at the output.
The coupling is part of the synchronizer assembly, which also includes a flange and a hub. Each synchronizer hub is connected to its shaft through splines and rotates with the shaft. Intermediate gears are installed on both sides of each synchronizer hub. Intermediate gears rotate freely on the shaft (except reverse gear). Each intermediate gear is in constant mesh with its drive gear. The synchronizer is located between the synchronizer hub and the intermediate gear.
The synchronizers are located on the shafts in the gearbox as follows:
- The 1st - 2nd gear synchronizer is located on the intermediate shaft 1st - 2nd, 5th -6th gears
- The synchronizer of 3rd - 4th gears is located on the intermediate shaft of 3rd - 4th gears
- Synchronizer 5th - 6th gear is located on the input shaft
- The reverse gear synchronizer is located on the reverse gear shaft
Synchronizer rings expand when heated, as do the elements with which they are in contact. As a consequence, no margin of safety is required to resist expansion. The intermediate gears of single and double synchronization do not have cones. This function is performed by the inner synchronizer ring.
Comments on this article