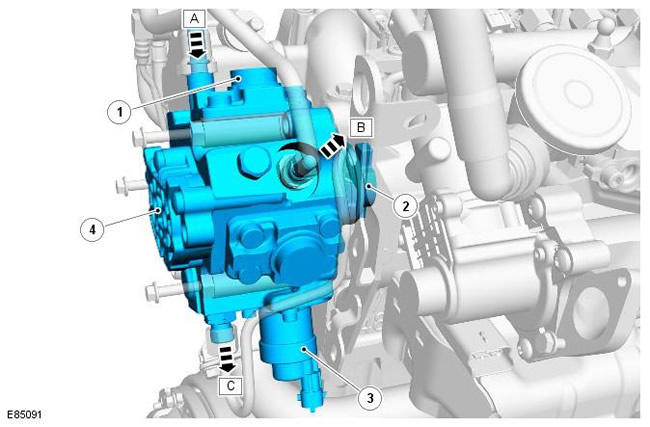
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| A | - | Fuel supply line from filter to suction pump |
| B | - | Low pressure fuel return to filter |
| C | - | High pressure fuel supply to the fuel manifold |
| 1 | - | High pressure plunger pairs (3 pcs.) |
| 2 | - | High pressure fuel pump drive shaft |
| 3 | - | VCV |
| 4 | - | suction pump |
The high pressure fuel pump is mounted behind the cylinder head (from the gearbox side) and is driven by the exhaust camshaft. The fuel pump is a 3-piston, radial plunger pump with plunger pairs evenly spaced around the circumference at 120 degrees to each other. The high pressure outlet port from the piston pairs connects to an annular circuit in the fuel pump and supplies constant pressure fuel to the fuel manifold. The pump is capable of generating a maximum fuel pressure of 1,600 bar.
The high pressure pump includes the following elements:
- Three high pressure plunger pairs
- Integrated suction pump
- Fuel control valve (VCV)
The high pressure fuel pump and the built-in suction pump are inseparable from each other. The high pressure fuel pump is not connected to the engine timing.
A controlled amount of fuel can be passed through the high pressure pump and returned through the fuel return line to the fuel filter. Returnable (bypassable) The fuel provides cooling and lubrication to the internal components of the high pressure fuel pump.
Suction pump
The fuel suction pump is mounted on the back of the fuel pump. It forms a single unit with the high pressure pump. The fuel suction pump is a gear type pump. It is connected to the fuel filter supply line. The suction pump creates a vacuum (subatmospheric pressure) in the supply line to the fuel tank and draws fuel from the tank. The fuel passes through the fuel filter and is then supplied under pressure from the suction pump to the inlet port of the high pressure pump.
Vacuum values for a normally operating suction pump are shown for the following engine operating conditions:
| Engine operating conditions | Vacuum created by the suction pump |
| cranking | -133±7 mbar |
| Full load | -267±133 mbar |
Fuel control valve (VCV)
The VCV is located on the high pressure pump. It is located in the supply port between the high pressure plunger pairs and the suction pump. VCV is a variable position solenoid valve that is controlled by the ECM via a pulse-width modulated signal (PWM) voltage 12V. The VCV controls the amount of fuel that is delivered by the suction pump to the high pressure plunger pairs.
During high pressure fuel pump operation, fuel pressure is built up when the VCV is open and the PCV mounted on the fuel rail is closed. The VCV and PCV valves have different positions and are used by the ECM to control fuel delivery and pressure in the fuel system.
During the fuel warm-up phase, when the fuel supply temperature is less than 40°C, the ECM fully opens the VCV. Fuel delivery and pressure are then controlled directly by the PCV under the control of the ECM.
The VCV is normally open when the solenoid valve is not receiving power from the ECM. The resistance value of the VCV solenoid coil is 2.8 ohms at 20°C. For more information see the chapter: Electronic Engine Controls - 2.2L Diesel (303-14 Electronic Engine Controls - 2.2L Diesel, Description and function).
Comments on this article