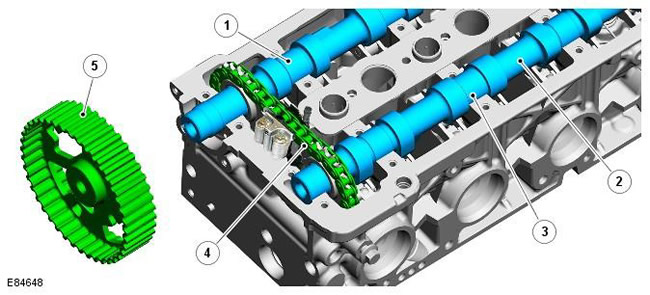
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | exhaust camshaft |
| 2 | - | intake camshaft |
| 3 | - | Bearing #3 (axial clearance control) |
| 4 | - | Single row timing chain |
| 5 | - | Camshaft Pulley |
The intake and exhaust camshafts are made of cast iron. Two camshafts are mounted between the camshaft cover and cylinder head, with each camshaft housed in five machined bearing housings. Liners are not used in bearing housings; camshafts rotate directly in aluminum bearings. The end play of the camshafts is controlled by the No. 3 camshaft bearing and is not adjustable. A bearing to ensure the correct axial clearance is an integral part of every camshaft.
NOTE: Camshaft end play is factory set between 0.070 mm and 0.168 mm. During maintenance, if the axial clearance is not correct, it may be necessary to replace the camshaft (ov) and/or cylinder heads and camshaft covers.
Each camshaft has 8 machined lobes arranged in pairs along the length of the camshaft. The camshaft lobes actuate the intake and exhaust valves via hydraulic lash adjusters and roller valve arms.
Each camshaft has a 19 tooth sprocket at the front end. The two sprockets are connected by a 40-link single row timing chain. The two camshaft sprockets have timing marks that align with the two colored links in the timing chain. A groove at the rear end of each camshaft is used to drive a flange-mounted vacuum pump and a high pressure fuel pump. The vacuum pump is driven by the intake camshaft; The high pressure fuel pump is driven by the exhaust camshaft.
The exhaust camshaft is driven by the crankshaft pulley through the timing belt. The exhaust camshaft pulley has 42 teeth and is keyed and bolted to the front end of the exhaust camshaft. The intake camshaft is driven by the exhaust camshaft via a single row chain.
The exhaust camshaft pulley has cutouts and a groove in the center hub. The cutouts form the impulse zone for the CMP sensor. The groove serves to install a special tool - a rod for adjusting the ignition timing. This special tool is used in combination with other special tools to adjust the position of the exhaust camshaft during ignition timing.
For more information on valve timing adjustment, see the appropriate service and repair procedures manual (SRP).
Valve timing adjustment
Valve timing values are shown in the following table:
| Valve | Position |
| Inlet valve opening | 15 degrees before TDC |
| Inlet valve closing | 12 degrees after BDC |
| Exhaust valve opening | 23 degrees before BDC |
| Closing the exhaust valve | 17 degrees after TDC |
Decryption:
- Before TDC = before top dead center
- After BDC = after bottom dead center
- Before BDC = before bottom dead center
- After TDC = after top dead center
Comments on this article