Tightening torques
| Description | Nm | lb-ft |
| Transmission fluid cooler bolts | 10 | 7 |
Ordinary climate
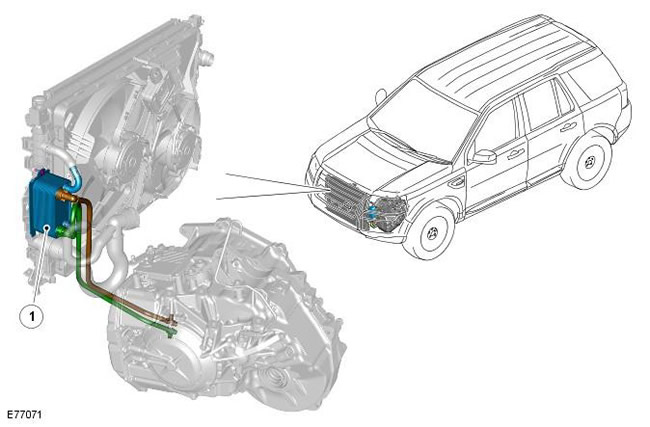
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | transmission fluid cooler |
Hot climate
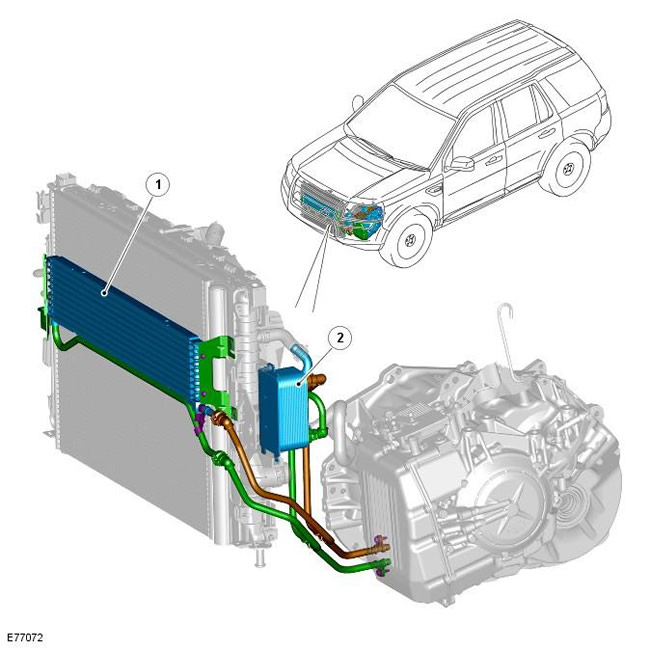
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Air-cooled transmission fluid cooler |
| 2 | - | Transmission fluid cooler cooled by engine coolant |
The AWF21 gearbox is equipped with an external fluid cooler that reduces the temperature of the transmission fluid.
In normal climate markets, a plate cooler is used, and the engine coolant is used to reduce the temperature of the working fluid.
In hot climate markets, in addition to the plate cooler for normal climates, an air blown cooler is used. It provides additional cooling at higher air temperatures, which are typical for these markets.
Cooler - normal climate
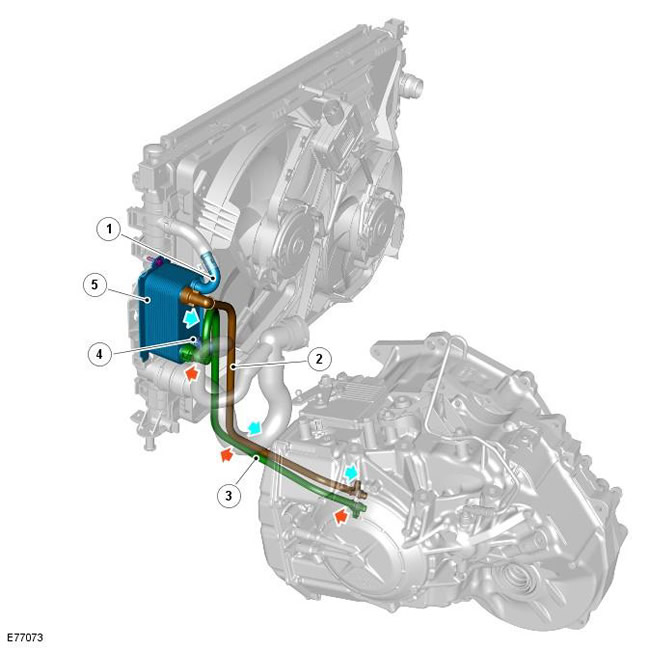
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Engine Coolant Inlet |
| 2 | - | Transmission Fluid Line - To Transmission |
| 3 | - | Transmission Fluid Line - From Transmission |
| 4 | - | Engine coolant outlet |
| 5 | - | transmission fluid cooler |
The transmission fluid cooler is mounted on the left side of the radiator. The liquid cooler consists of an aluminum housing containing louvre fins and plates. The plates allow the transverse flow of transmission fluid and engine coolant through the cooler. The plates are immersed in engine coolant with "cold" side of the radiator, which cools the transmission fluid by using the temperature difference between the transmission fluid and the engine coolant.
In the engine cooling system, the low-temperature zone is located in the upper third of the radiator. The flow of engine coolant through this radiator section is restricted by the transmission fluid cooler. Therefore, the engine coolant in this section of the radiator flows through the cooling pipes at a slower rate. Here, the engine coolant cools more than in the lower section of the radiator, and therefore provides increased transmission fluid cooling.
The transmission fluid pump delivers transmission fluid to the lower cooler port. After passing through the cooler, the transmission fluid exits through the top port and returns to the transmission oil pan.
Cooler - hot climate
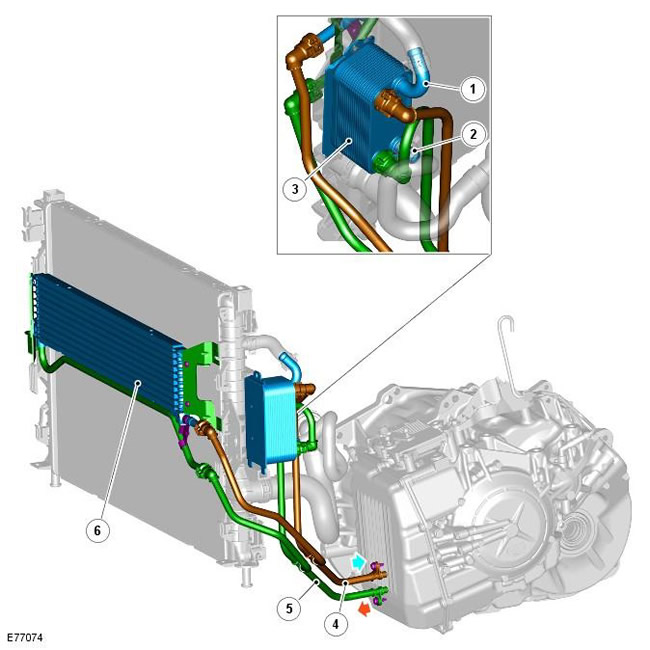
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Engine Coolant Inlet |
| 2 | - | Engine coolant outlet (hidden) |
| 3 | - | Transmission fluid cooler cooled by coolant |
| 4 | - | Transmission Fluid Line - To Transmission |
| 5 | - | Transmission Fluid Line - From Transmission |
| 6 | - | Air-cooled transmission fluid cooler |
For countries with hot climates, the transmission fluid cooling system uses the same coolant as the standard cooling system, but with an additional air-cooled cooler that is located in front of the air conditioning radiator and condenser.
This fluid cooler functions in the same way as the conventional climate cooler described. The air blown cooler has two end tanks connected with hollow plates. The plates allow the transmission fluid to flow from one end tank to the other, and the air flowing around the plates cools the transmission fluid.
At the pump outlet, the transmission fluid is separated between the conventional coolant and the air-cooled cooler. Some of the transmission fluid flows from the pump to the air-cooled cooler. The liquid passes through the cooler plates and is cooled by the air flow that flows around the plates. The transmission fluid is then directed to the T-connection to the liquid line of the standard cooler, after which it returns to the transmission.
Comments on this article