Solenoid valves
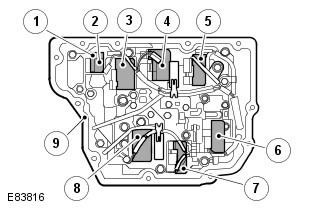
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | 3-way solenoid valve - S1 |
| 2 | - | 3-way solenoid valve - S2 |
| 3 | - | Line pressure control solenoid valve - SLT |
| 4 | - | Shift Control Solenoid Valve - SLC2 |
| 5 | - | Shift Control Solenoid Valve - SLC1 |
| 6 | - | Lockout Control Solenoid Valve - SLU |
| 7 | - | Shift Control Solenoid Valve - SLC3 |
| 8 | - | Shift control solenoid valve - SLB1 |
| 9 | - | valve block |
Shift Control Solenoid Valves - SLC1, SLC2, SLC3, SLB1
Shift Control Solenoid Valves (SLC1, SLC2, SLC3 and SLB1) mounted on the front valve body. Solenoid valves respond to input from the TCM and control the hydraulic pressure applied to the clutches (C1, C2 and C3) and brake B1, to ensure smooth shifting. TCM uses these solenoid valves alone or in combination with each other to provide shifting from 1st to 6th gear.
If the solenoid valve fails, the TCM cuts off current to the shift control solenoid valves and the transmission goes into failsafe mode to prevent damage.
Line pressure control solenoid valve - SLT
Line pressure control solenoid valve (SLT) mounted on the front valve body. The solenoid valve is controlled in-line by the TCM, which uses throttle position signals and engine torque information from the engine control module (ECM), to calculate the operating parameters of the solenoid valve. The solenoid valve controls line pressure to the clutches and brakes to ensure smooth shifting.
If the solenoid valve fails, the TCM stops supplying current to it. Maximum pressure will be applied to the clutches and brakes unless the fault is caused by a stuck solenoid valve that could cause low line pressure.
Lockout Control Solenoid Valve - SLU
The lockout control solenoid valve is mounted on the front valve body. The solenoid valve is controlled in-line by the TCM, which uses engine speed, throttle opening degree, and transmission speed sensor signals to calculate solenoid valve operation parameters. The solenoid valve controls the amount of lockup or slippage required by the torque converter lock-up clutch.
If the solenoid valve fails, the TCM stops supplying current to it, resulting in the torque converter not locking up.
3-way solenoid valve - S1, S2
3-way solenoid valve (S1) located on the central valve body, and the solenoid valve (S2) - on the front valve body. The solenoid valves are on/off solenoid valves controlled by the TCM. A combination of 2 solenoid valves is used to either control engine braking in 1st gear or to shift gears.
If the solenoid valve fails, the TCM stops supplying current to both solenoid valves.
Speed sensors
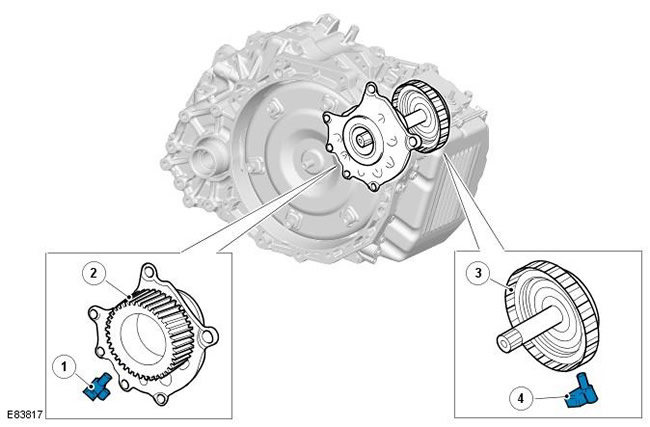
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Speed sensor (SP) - frequency of rotation of the output shaft |
| 2 | - | Reverse drive gear |
| 3 | - | Clutch drum C2 |
| 4 | - | Speed sensor (NIN) |
The gearbox uses two speed sensors (NIN and SP), located in the gearbox housing. Speed sensor (SP) located next to the reverse drive gear and reads the gear teeth to generate an output signal of the output shaft speed. Speed sensor (NIN) located next to the clutch drum C" and reads the teeth on the outer circumference of the drum to generate an input shaft speed output. Both speed signals are received by the TCM, which uses the two signals to calculate engine output torque, shift time, and torque converter lockup.
Transmission fluid temperature sensor
The transmission fluid temperature sensor is located on the internal wiring harness in the transmission. It detects the temperature of the transmission fluid in the hydraulic pressure control circuit and transmits a signal corresponding to the temperature to the TCM. The TCM monitors temperature and ensures smooth shifting over a wide temperature range.
Comments on this article