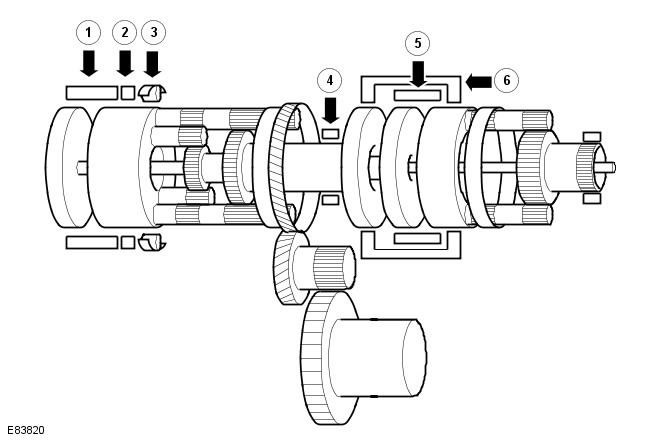
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Coupling - C2 |
| 2 | - | Brake - B2 |
| 3 | - | One way clutch - F1 |
| 4 | - | Brake - B1 |
| 5 | - | Coupling - C1 |
| 6 | - | Coupling - C3 |
X = work
Power flow - 1st gear, engine braking
Solenoid valve operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Solenoid valve | ||||||
| SLC 1 | SLC 2 | SLC 3 | SLB 1 | S1 | S2 | ||
| D | Engine brake | - |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
Clutch and brake operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Coupling | Brake | One way clutch | ||||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | B1 | B2 | F1 | ||
| D | Engine brake | X |
- |
- |
- |
X |
X |
When the engine brake is applied, the driving force is transmitted to the gearbox from the wheels through the power transmission unit. Rear planetary carrier blocked by one-way clutch (F1) and brake (B2) from clockwise rotation. This causes torque from the wheels to be transferred directly to the engine, providing engine braking.
Power flow - 1st gear
Solenoid valve operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Solenoid valve | ||||||
| SLC 1 | SLC 2 | SLC 3 | SLB 1 | S1 | S2 | ||
| D | 1st gear | - |
X |
X |
X |
- |
- |
Clutch and brake operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Coupling | Brake | One way clutch | ||||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | B1 | B2 | F1 | ||
| D | 1st gear | X |
- |
- |
- |
- |
X |
The planetary gears are in the following states:
- Front planetary gear
- Input: Ring gear
- Locked: Sun gear
- Output: Carrier
- Rear planetary gear
- Input: Rear sun gear
- Blocked: Carrier
- Output: Ring gear
Front planetary gear
The input shaft is driven by a torque converter and rotates clockwise. The planetary ring gear rotates clockwise along with the planet gear, which also rotates clockwise around its axis and orbit. The planetary sun gear is locked by a hydraulic pump that presses it against the planetary ring gear and orbits the sun gear around its axis.
The front planetary carrier rotates clockwise in the same direction as the planetary gear. Coupling (C1) engaged and locks the planetary carrier against the rear planetary sun gear.
Rear planetary gear
The planetary sun gear rotates clockwise. The short satellite rotates counterclockwise. Planet carrier tries to rotate in the same direction but is held back by a one-way clutch (F1).
The long planet gear rotates clockwise around its axis, and the middle sun gear rotates counterclockwise idle. The ring gear is rotated by a long pinion and drives the reverse drive gear, which rotates counterclockwise.
The reverse driven gear is driven counterclockwise and in turn drives the differential ring gear clockwise.
Power flow - 2nd gear
Solenoid valve operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Solenoid valve | ||||||
| SLC 1 | SLC 2 | SLC 3 | SLB 1 | S1 | S2 | ||
| D | 2nd gear | - |
X |
X |
- |
- |
- |
Clutch and brake operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Coupling | Brake | One way clutch | ||||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | B1 | B2 | F1 | ||
| D | 2nd gear | X |
- |
- |
X |
- |
- |
The planetary gears are in the following states:
- Front planetary gear
- Input: Ring gear
- Locked: Sun gear
- Output: Carrier
- Rear planetary gear
- Input: Rear sun gear
- Locked: Middle sun gear
- Output: Ring gear
Front planetary gear
The input shaft is driven by a torque converter and rotates clockwise. The planetary ring gear rotates clockwise along with the planet gear, which also rotates clockwise around its axis and orbit. The planetary sun gear is locked by a hydraulic pump that presses it against the planetary ring gear and orbits the sun gear around its axis.
The front planetary carrier rotates clockwise in the same direction as the planetary gear. Coupling (C1) engaged and locks the planetary carrier against the rear planetary sun gear.
Rear planetary gear
The planetary sun gear and carrier rotate clockwise. The middle sun gear is blocked by a brake (IN 1). Short satellites rotate counterclockwise around their axis and move in an orbit in a clockwise direction. Long satellites rotate clockwise around their axis and their orbit.
The ring gear rotates clockwise with a long pinion. The ring gear and reverse drive gear rotate clockwise.
The reverse driven gear is driven counterclockwise and in turn drives the differential ring gear clockwise.
NOTE: Engine braking is available when this gear is selected.
Power flow - 3rd gear
Solenoid valve operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Solenoid valve | ||||||
| SLC 1 | SLC 2 | SLC 3 | SLB 1 | S1 | S2 | ||
| D | 3rd gear | - |
X |
- |
X |
- |
- |
Clutch and brake operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Coupling | Brake | One way clutch | ||||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | B1 | B2 | F1 | ||
| D | 3rd gear | X |
- |
- |
X |
- |
- |
The planetary gears are in the following states:
- Front planetary gear
- Input: Ring gear
- Locked: Sun gear
- Output: Carrier
- Rear planetary gear
- Input: Medium sun gear
- Blocked: -
- Output: Ring gear
Front planetary gear
The input shaft is driven by a torque converter and rotates clockwise. The planetary ring gear rotates clockwise along with the planet gear, which also rotates clockwise around its axis and orbit. The planetary sun gear is locked by a hydraulic pump that presses it against the planetary ring gear and orbits the sun gear around its axis.
The front planetary carrier rotates clockwise in the same direction as the planetary gear. Coupling (C1) engaged and locks the planetary carrier against the rear planetary sun gear. Coupling (C3) is also engaged and blocks the carrier with respect to the middle sun gear.
Rear planetary gear
The short planetary gear and the long satellite gear are engaged, which leads to blocking of both satellites due to the different direction of rotation. Torque from the sun gear and middle sun gear is transmitted to the ring gear, which rotates clockwise in the same direction as the planetary carrier.
The reverse drive gear rotates clockwise with the ring gear.
The reverse driven gear rotates counterclockwise and in turn drives the differential ring gear clockwise.
NOTE: Engine braking is available when this gear is selected.
Power flow - 4th gear
Solenoid valve operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Solenoid valve | ||||||
| SLC 1 | SLC 2 | SLC 3 | SLB 1 | S1 | S2 | ||
| D | 4th gear | - |
- |
X |
X |
- |
- |
Clutch and brake operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Coupling | Brake | One way clutch | ||||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | B1 | B2 | F1 | ||
| D | 4th gear | X |
X |
- |
- |
- |
- |
The planetary gears are in the following states:
- Front planetary gear
- Input: Ring gear
- Locked: Sun gear
- Output: Carrier
- Rear planetary gear
- Input: Rear sun gear, carrier
- Blocked: -
- Output: Ring gear
Front planetary gear
The input shaft is driven by a torque converter and rotates clockwise. The planetary ring gear rotates clockwise along with the planet gear, which also rotates clockwise around its axis and orbit. The planetary sun gear is locked by a hydraulic pump that presses it against the planetary ring gear and orbits the sun gear around its axis.
The front planetary carrier rotates clockwise in the same direction as the planetary gear. Coupling (C1) engaged and locks the planetary carrier against the rear planetary sun gear. The intermediate shaft rotates in the same direction as the input shaft. Coupling (C2) is also engaged and rotates in the same direction as the intermediate shaft.
Rear planetary gear
The planetary carrier rotates clockwise along with the intermediate shaft. The short satellite rotates clockwise around its axis and orbits at a higher speed than the sun gear. The long satellite rotates counterclockwise around its axis and orbit. The ring gear rotates clockwise more slowly than the carrier due to the fact that the carrier prevents the rotation of the long pinion.
The reverse drive gear rotates clockwise with the ring gear.
The reverse driven gear rotates counterclockwise and in turn drives the differential ring gear clockwise.
NOTE: Engine braking is available when this gear is selected.
Power flow - 5th gear
Solenoid valve operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Solenoid valve | ||||||
| SLC 1 | SLC 2 | SLC 3 | SLB 1 | S1 | S2 | ||
| D | 5th gear | X |
- |
- |
X |
- |
- |
Clutch and brake operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Coupling | Brake | One way clutch | ||||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | B1 | B2 | F1 | ||
| D | 5th gear | - |
X |
X |
- |
- |
- |
The planetary gears are in the following states:
- Front planetary gear
- Input: Ring gear
- Locked: Sun gear
- Output: Carrier
- Rear planetary gear
- Input: Medium sun gear
- Blocked: -
- Output: Ring gear
Front planetary gear
The input shaft is driven by a torque converter and rotates clockwise. The planetary ring gear rotates clockwise along with the planet gear, which also rotates clockwise around its axis and orbit. The planetary sun gear is locked by a hydraulic pump that presses it against the planetary ring gear and orbits the sun gear around its axis.
The front planetary carrier rotates clockwise in the same direction as the planetary gear. Coupling (C3) engaged and locks the planetary carrier against the rear planetary middle sun gear. The intermediate shaft rotates in the same direction as the input shaft. Coupling (C2) is also engaged and rotates in the same direction as the intermediate shaft.
Rear planetary gear
The middle sun gear rotates clockwise in the same direction as the clutch (C3). Braking the front planetary gear slows down the speed of rotation of the input shaft. The intermediate shaft rotates clockwise in the same direction as the input shaft. The planetary carrier also rotates clockwise in the same direction as the intermediate shaft.
The long satellite rotates clockwise around its axis and orbit. The carrier rotates faster than the middle sun gear, which balances the middle pinion with the difference in speed. The middle satellite moves in orbit and rotates clockwise around its axis.
The planetary ring gear rotates clockwise. The ring gear rotates faster than the planetary carrier because the rotation of the long pinion is coupled with the speed of the planetary carrier. The reverse drive gear rotates clockwise with the ring gear.
The reverse driven gear rotates counterclockwise and in turn drives the differential ring gear clockwise.
NOTE: Engine braking is available when this gear is selected.
Power flow - 6th gear
Solenoid valve operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Solenoid valve | ||||||
| SLC 1 | SLC 2 | SLC 3 | SLB 1 | S1 | S2 | ||
| D | 6th gear | X |
- |
X |
- |
- |
- |
Clutch and brake operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Coupling | Brake | One way clutch | ||||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | B1 | B2 | F1 | ||
| D | 6th gear | - |
X |
- |
X |
- |
- |
The planetary gears are in the following states:
- Front planetary gear
- Entrance: -
- Blocked: -
- Exit: -
- Rear planetary gear
- Input: carrier
- Locked: Middle sun gear
- Output: Ring gear
Front planetary gear
The input shaft is driven by a torque converter and rotates clockwise. The intermediate shaft rotates clockwise in the same direction as the torque converter. Coupling (C2) blocks the intermediate shaft in relation to the carrier of the rear planetary gear.
Rear planetary gear
The planetary carrier rotates clockwise in the same direction as the intermediate shaft. The long satellite rotates clockwise around its axis and orbit. The speed of rotation of the middle sun gear increases with the speed of the input shaft because it is locked.
The planetary ring gear rotates clockwise. The ring gear rotates faster than the planetary carrier because the rotation of the long pinion is coupled with the speed of the planetary carrier. The reverse drive gear rotates clockwise with the ring gear.
The reverse driven gear rotates counterclockwise and in turn drives the differential ring gear clockwise.
NOTE: Engine braking is available when this gear is selected.
Power flow - reverse gear
Solenoid valve operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Solenoid valve | ||||||
| SLC 1 | SLC 2 | SLC 3 | SLB 1 | S1 | S2 | ||
| R | Reverse gear - less than 11 V | X |
X |
- |
X |
- |
- |
| R | Reverse gear - more than 11 V | X |
X |
X |
X |
- |
- |
Clutch and brake operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Coupling | Brake | One way clutch | ||||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | B1 | B2 | F1 | ||
| R | Reverse gear - less than 11 V | - |
X |
- |
X |
- |
- |
| R | Reverse gear - more than 11 V | - |
- |
- |
- |
X |
- |
The planetary gears are in the following states:
- Front planetary gear
- Input: Ring gear
- Locked: Sun gear
- Output: Carrier
- Rear planetary gear
- Input: Medium sun gear
- Blocked: Carrier
- Output: Ring gear
Front planetary gear
The input shaft is driven by a torque converter and rotates clockwise. The planetary ring gear rotates clockwise with the input shaft.
The satellite rotates clockwise around its axis and orbit. The planetary sun gear is locked by a hydraulic pump that presses it against the planetary ring gear and orbits the sun gear around its axis. The planetary carrier rotates clockwise along with the planetary gear moving in orbit.
Coupling (C3) engaged and rotates clockwise and locks the planetary carrier against the rear planetary middle sun gear.
Rear planetary gear
The middle sun gear rotates clockwise along with the clutch (C3), but at a lower speed than the input shaft. Brake (AT 2) is activated and blocks the planetary carrier. The long pinion rotates counterclockwise and in turn rotates the ring gear counterclockwise.
The reverse drive gear rotates counterclockwise with the ring gear at the same speed.
The reverse driven gear rotates clockwise and in turn drives the differential ring gear counterclockwise.
NOTE: Engine braking is available when this gear is selected.
Power flow in neutral
Solenoid valve operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Solenoid valve | ||||||
| SLC 1 | SLC 2 | SLC 3 | SLB 1 | S1 | S2 | ||
| N | Neutral gear | X |
X |
X |
X |
- |
- |
Clutch and brake operation:
| Gear selector lever position | Coupling | Brake | One way clutch | ||||
| C1 | C2 | C3 | B1 | B2 | F1 | ||
| N | Neutral gear | - |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
In neutral, all solenoid valves are energized except for 3-way solenoid valves; all clutches and brakes are disengaged. This allows the input shaft to rotate the front planetary gear without transferring torque to the differential ring gear.
Comments on this article