Steering gear
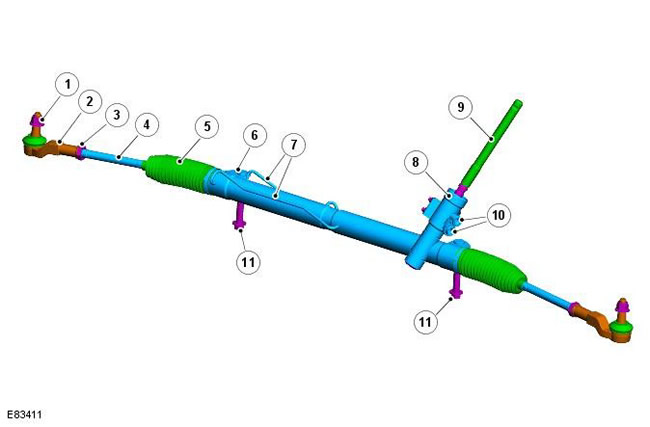
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Lock-nut |
| 2 | - | Tie rod end |
| 3 | - | Lock-nut |
| 4 | - | Tie Rod |
| 5 | - | Steering gear cover |
| 6 | - | Elements of fastening of the case of the steering mechanism. |
| 7 | - | Discharge/return pipelines |
| 8 | - | Valve body |
| 9 | - | input shaft |
| 10 | - | Discharge/return connection to/from pump |
| 11 | - | Mounting bolts |
The Visteon-made steering gear is located at the rear of the front subframe on the upper side. It is securely attached to the subframe with two bolts. Bolts are omitted from the underside of the subframe for ease of access for maintenance. They are screwed into threaded bushings on the steering gear housing.
The steering gear is a selection block of a traditional design, rack and pinion type, with an amplifier; the number of turns between the extreme positions of the lock - 2.6. Steering gear ratio (the ratio of the angle of rotation of the steering wheel and the drive wheels) is 16.7:1, which provides a very fast and clear response to the driver's commands. The steering gear has large diameter tie rods that optimize feedback and control of the driver over the vehicle.
The steering gear includes a steel welded and machined one-piece housing containing the steering rack, valve block and integral hydraulic unit. The gear rack of the steering mechanism with the piston fixed to it moves in the mechanism housing along the guide bushings. The drive gear, connected to the valve block, meshes with the rack and is supported by bearings. The toothed rack is pressed against the gear with a spring-loaded fork, which ensures backlash-free engagement of the gear and rack. The gear is connected to the valve block using a torsion bar. The rotational movement of the steering wheel is converted by the gear-rack transmission into a linear movement of the rack. In this case, the booster valve block is activated. This movement is converted by means of adjustable tie rods into wheel movement.
The hydraulic block piston is located at one end of the steering gear housing. On both sides of the piston there is a pressure chamber and a return chamber, which are connected to the valve block by means of external metal pipelines. At each end of the mechanism there is a threaded hole that serves to install the tie rod. The outer ends of the steering box are protected by covers that prevent the ingress of dirt and moisture and allow vertical movement of the tie rods with respect to the suspension in addition to linear movement when the steering wheel is turned. The covers are serviceable elements and are fixed to the mechanism body and tie rod ends with the help of clamps.
Comments on this article