Location of elements
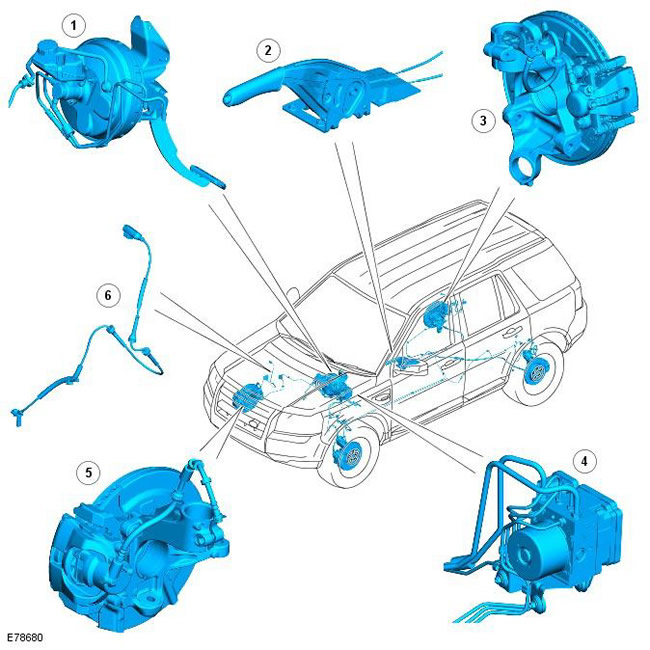
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Brake pedal, brake booster and master cylinder assembly |
| 2 | - | Parking brake lever |
| 3 | - | Rear brake disc assembly with parking brake |
| 4 | - | Anti-Lock Braking System Module (ABS) and hydraulic control unit (HCU) |
| 5 | - | Front disc brake assembly |
| 6 | - | ABS speed sensor wire |
Vehicle braking is provided by a vacuum-assisted hydraulic drive. The hydraulic drive is connected through the ABS module assembly with the HCU to the front and rear brake calipers. To increase safety, the hydraulic system has a two-circuit scheme with diagonal separation. The hydraulic drive consists of primary and secondary brake circuits. Each circuit runs between the master cylinder and each front and opposite rear wheel.
The braking system is equipped with an anti-lock braking system, which should help the driver to control the car in all driving and maneuvering conditions. Sophisticated ABS functionality also integrates with other systems controlled by the vehicle's software to facilitate off-road stability and control.
The parking brake is a mechanical cable operated system that acts on the brake pads located inside each rear brake disc.
Front and rear disc brakes
The 3.2L i6 is equipped with ventilated front and rear disc brakes. The 2.2L TD4 is equipped with ventilated front and solid rear disc brakes. On i6 and TD4 vehicles, all disc brakes use single piston and floating calipers. For more information, see the chapter:
- Front disc brake (206-03 Front disc brake, description and principle of operation)
- Rear disc brake (206-04 Rear Disc Brake Description and Operation)
Parking brake
The parking brake is a cable operated system with manual activation. Brake drums are built into the right and left rear brake discs, in which the pads and parking brake elements are located. For more information, see chapter: Parking brake (206-05 Parking brake and parking brake actuator, Description and function).
Hydraulic brake
The hydraulic brake actuator consists of the brake pedal, master cylinder, HCU and connecting hydraulic lines and hoses. The tandem brake master cylinder with reservoir is attached to and actuated by the vacuum brake booster. The brake master cylinder has a tandem design and supplies pressure to two independent hydraulic circuits (primary and secondary).
For more information, see chapter: Hydraulic brakes (206-06 Hydraulic brakes, Description and principle of operation).
Vacuum brake booster
The vacuum brake booster uses vacuum to operate. It serves to increase the efficiency of the hydraulic brakes. The amplifier has a tandem design that includes two separate diaphragms. On both petrol and diesel models, the vacuum required to operate the booster is generated by a vacuum pump driven by the engine.
For more information, see chapter: Vacuum Brake Booster (206-07 Vacuum brake booster, Description and principle of operation).
Anti-Lock Braking System
The ABS system is equipped with a Continental Teves Mk25E1 ABS module with an integrated 4-channel HCU. The ABS module and HCU provide control over the braking system and also provide active braking functions to control the vehicle's directional stability and traction. The ABS module also provides special functions to make driving easier when driving in off-road conditions.
The anti-lock braking system provides the following features:
- Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS)
- Corner braking system (CBC)
- Vehicle Dynamic Stability Control (DSC)
- Electronic brake force distribution (EBD)
- Electronic traction control (ETC)
- Emergency Brake Assist (EBA)
- Motor braking torque control (EDC)
- Descent control system (HDC) with gradual release
- roll control (RSC)
- Terrain Response™ System Integration
For more information, please refer to the chapter: Anti-Lock Braking System - Heading Stability Function (206-09C Anti-Lock Braking System - Heading Stability Function, Description and Operation).
Comments on this article