Dismantling
1. Remove the cylinder head.
ENGINE - MODIFICATION K, volume 1.8, Piston group, Cylinder head gasket.
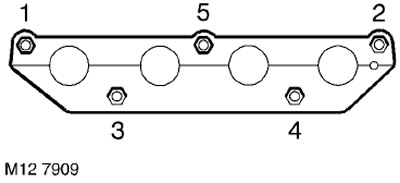
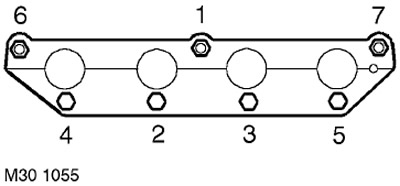
2. In the sequence shown in the figure, loosen and unscrew the 5 nuts securing the exhaust manifold to the cylinder head and remove the manifold.
3. Remove and discard the exhaust manifold gasket.
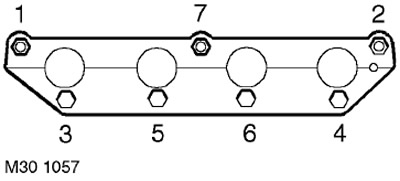
4. In the sequence shown in the figure, loosen and unscrew the 7 nuts securing the intake manifold to the cylinder head.
5. Remove the intake manifold and discard its gaskets.
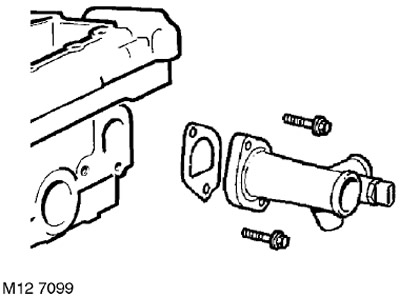
6. Turn away 2 bolts of fastening of an output cranked branch pipe of the cooling system to heads of cylinders. Remove the nozzle and discard the gasket.
7. Turn out spark plugs.
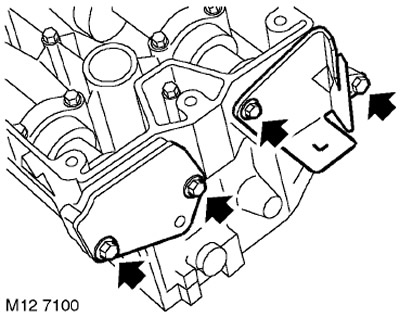
8. Turn away 4 bolts of fastening of forward and back covers of cam-shaft epiploons and remove covers.
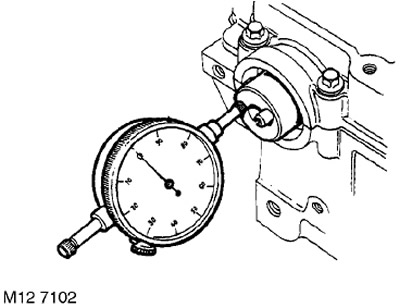
9. Check the camshaft end play using a dial gauge.
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS, Engine - gasoline K1.8.
10. If the axial exceeds the allowable value, then install a new shaft (or new shafts) and check with them, if the play is still too high, then replace the camshaft cover with cylinder head assembly.
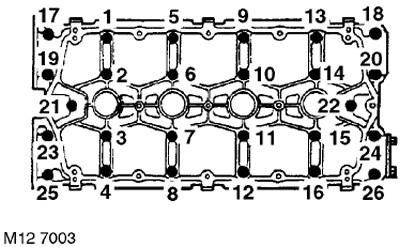
11. Gradually, in the sequence shown in the figure, loosen the 26 bolts securing the camshaft cover so that the valve springs are completely unloaded.
12. Remove the camshaft cover.
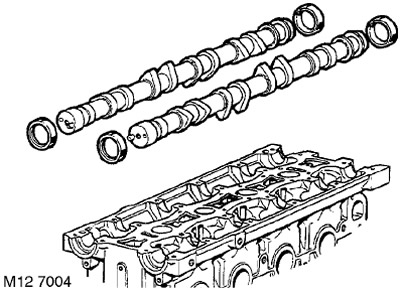
13. Mark the location of the camshafts and remove the intake and exhaust camshafts. Remove the 4 oil seals from the shafts and discard the oil seals.
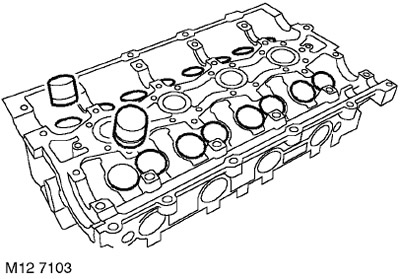
14. Using a magnet, remove 16 hydraulic lifters from the cylinder head. Hydraulic lifters must be stored in the order in which they were installed and, at the same time, be upside down so that oil does not leak out of them.
15. Check expansion joints for wear, nicks and overheating.
16. Measure the diameter of each expansion joint. The measurement is made in the middle chord of the compensator.
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS, Engine - gasoline K1.8.
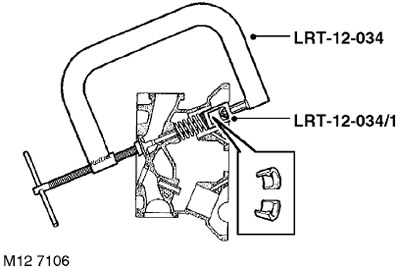
17. Using the LRT-12-034 cracker with the LRT-12-034/1 tip, compress the valve springs, remove two crackers, release the spring and remove the LRT-12-034 cracker.
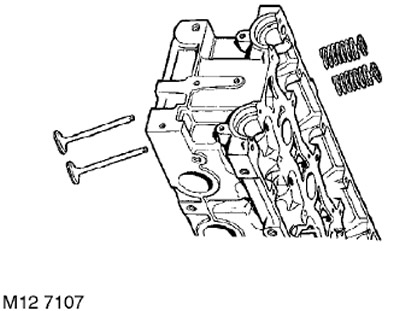
18. Remove the valve spring with the top plate.
19. Remove the valve from the cylinder head.
20. Using the LRT-12-071 tool, remove and discard the valve stem seal.
21. Repeat with the rest of the valves, laying out the valves with springs in the order in which they were installed on the cylinder head.
22. Lay the cylinder head on the plane to which the intake manifold is attached, and place wooden blocks.
23. Carry out the operations described above with final valves.
24. Wipe the camshafts, bearing surfaces of the camshaft journals in the bed, mating surfaces of the camshaft bed and cylinder heads.
25. Check the condition of the camshafts. If they are scratched, dented, or excessively worn, replace the camshafts.
26. Lay the camshafts in the cylinder head and apply a strip of deformable caliber to each of the necks.
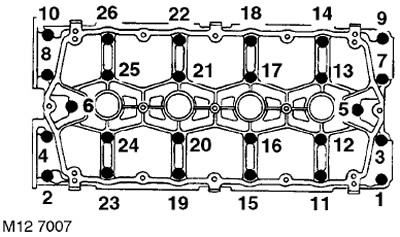
27. Install the camshaft cover and gradually, in the sequence shown in the figure, tighten the bolts to a torque of 10 Nm. DO NOT ROTATE the camshafts.
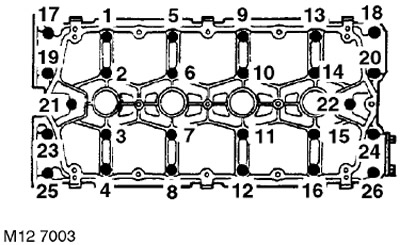
28. In the sequence shown in the figure, loosen and unscrew the bolts securing the camshaft cover.
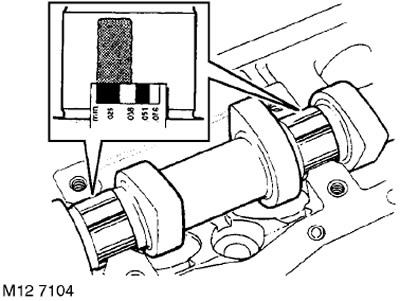
29. Measure the widest part of each gauge strip: Gap size = 0.060 - 0.094 mm. Maximum allowable clearance = 0.15 mm.
30. If the gap is greater than the allowable, then put new shafts and repeat the check. If the clearance is still too large, replace the cylinder head.
31. With a rag soaked in oil, remove all traces of a deformable caliber from the necks.
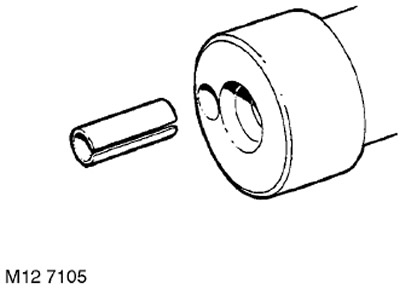
32. If an old shaft is installed, then remove the pin from it and install a new one, with a cut to the axis of the shaft.
33. Wipe the camshaft gears, check the condition of the teeth and pin holes for wear.
WARNING: If sintered gears (powder metallurgy technology), have been in contact with oil for a long time, then, before installation, they must be soaked in a solvent and then washed in a pure solvent.
34. Clean the mating surfaces of the integral camshaft cover and cylinder head. Wipe the surfaces under the intake and exhaust manifolds.
CAUTION: Do not use a metal scraper.
35. Clear a deposit from a deposit the lower plane of a head of cylinders.
36. Blow out the oil channels and channels of the cooling system.
37. Check up a head of cylinders regarding damages, pay special attention to the bottom plane of a head of cylinders.
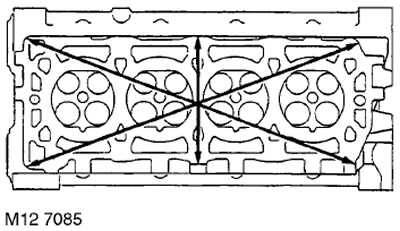
38. Check the plane of the cylinder head for warping by laying a straightedge along the directions shown in the figure.
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS, Engine - gasoline K1.8.
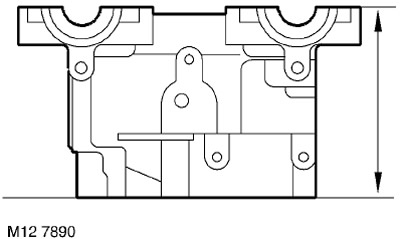
39. Check up height of a head of cylinders.
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS, Engine - gasoline K1.8.
NOTE: The underside of the cylinder head may be ground as long as the head height remains within acceptable limits.
40. Check the condition of the valve springs and measure the free height of the springs.
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS, Engine - gasoline K1.8.
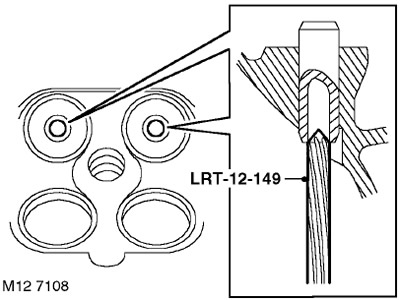
41. Use LRT-12-149 to remove carbon from the exhaust valve guides.
ATTENTION: The device is inserted into the sleeve from the side of the lower plane of the cylinder head.
42. Remove carbon deposits from the inlet valve guides, inlet and outlet valves, valve seats, and firing surface of the head. After completing the descaling procedure, blow out the head to remove all particles.
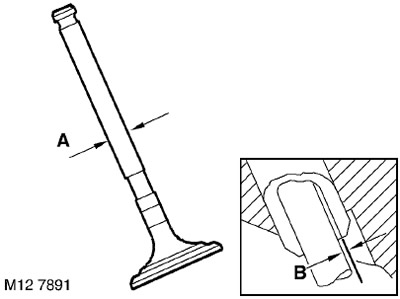
43. Measure and record the stem diameters 'A' of the old valves, replace the valve if the stem diameter is less than acceptable.
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS, Engine - gasoline K1.8.
44. Using the procedure below, measure clearances 'B' between the intake and exhaust valve stems and their guides.
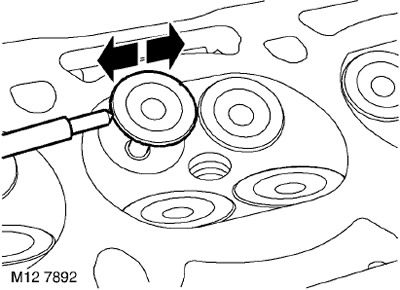
45. Insert the valve into the appropriate sleeve.
46. Pull the valve disc 10 mm up and install the dial indicator as shown in the figure.
47. Move the valve disc to the front of the cylinder head and set "zero" indicator, making sure that the indicator leg remains pressed against the plate.
48. Move valve to rear of cylinder head and read indicator 'B'
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS, Engine - gasoline K1.8.
49. Repeat this operation with each of the valves.
CAUTION: Store the cylinder head bolts in the order in which they were on the assembled engine.
50. Replace valves and valve guides if necessary.
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS, Engine - gasoline K1.8.
51. Lay the cylinder head on wooden blocks.
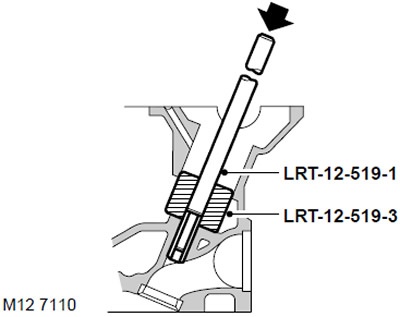
52. Insert drift LRT-12-519-3 into the pusher socket and knock out the bushing using the LRT-12-519-1 drift.
NOTE: Lay out the valve guides in the same order as they were on the assembled engine.
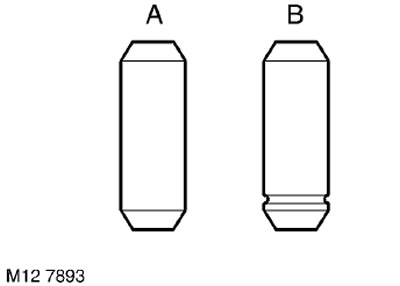
53. Determine the type of bushings installed: 'A' - Factory assembled 'B' - Replaced in service.
WARNING: Factory installed bushings 'A' must be replaced with repair bushings 'B'.
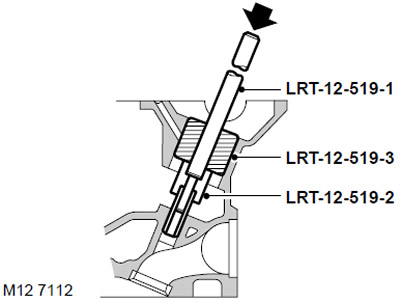
54. Install the valve guide into the guide seat, with the groove toward the valve seat, and install the LRT-12-519-2 stopper onto the guide.
NOTE: When replacing bushings, the cylinder head and bushing must be at room temperature.
55. Install the LRT-12-519-3 kapron mandrel into the compensator socket and drive the sleeve with the LRT-12-519-1 mandrel until the limiter reaches the surface of the cylinder head.
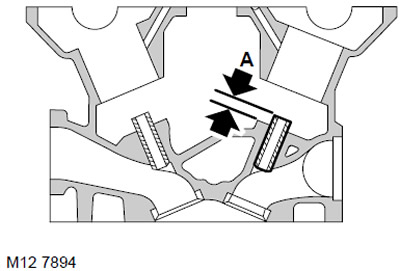
56. Measure protrusion 'A' of valve guide: = 6.00 mm.
57. Check the condition of the valve seats and those valves that are to be reused.
58. Replace valve seats if necessary.
CAUTION: Be careful when removing the seats to avoid damaging the seating surface.
59. Cool the new seats in liquid nitrogen and install them immediately in the cylinder head.
CAUTION: Do not heat the cylinder head. Saddles after chamfering should not protrude above the lower plane of the cylinder head.
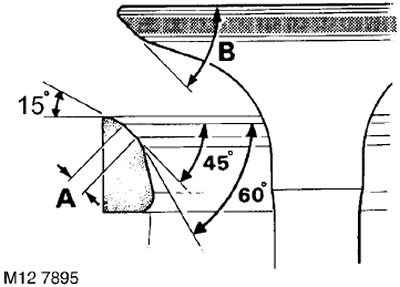
60. Cut the bevels of the saddles with a special cutter with a pilot, while ensuring the following angles of inclination:
- 15°. - First cut
- 45°. - Final cut with deburring
- 60°. - Trimming to obtain the desired chamfer width
61. Check the width of the chamfer of the valve and its angle of inclination:
- Chamfer Width 'A' - Inlet = 1.2mm; Outlet = 1.6mm
- Valve Angle 'B' - Inlet and Outlet = 45°.
62. Lap the valve faces using a fine-grained lapping paste.
63. Apply a thin layer of Prussian blue to the bevel of the valve seat, insert the valve into the guide and press it without turning it. Remove the valve and check the uniformity and position of the fit by looking at the imprint. The ink should be printed along the centerline of the bevel.
64. Lap in and recheck the fit of the bevel.
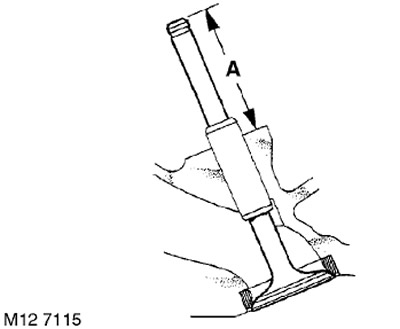
65. Check valve stem protrusion 'A'.
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS, Engine - gasoline K1.8.
66. If the valve stem protrudes more than allowed, install a new valve and check the stem protrusion again. If this measure does not help, then replace the valve seat.
Installation
1. Wash the intake and exhaust valves, spring plates, crackers and valve springs.
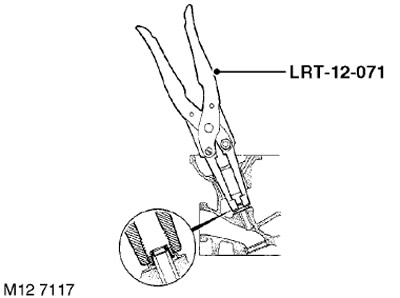
2. Lubricate the new valve stem seal with clean engine oil and install it on the valve guide using the LRT-12-071 tool.
3. Lubricate the valve with clean engine oil and insert it into the guide.
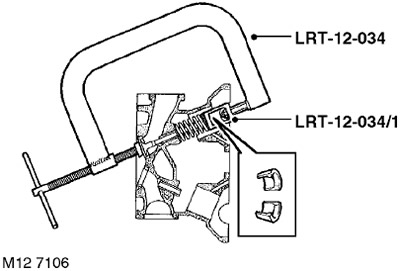
4. Install the spring with the plate, compress the spring with the LRT-12-034 cracker with the LRT-12-034/1 tip, install the crackers.
5. Repeat the procedure for the rest of the valves.
6. Through a wooden block, hit the end of the valve stem two or three times so that the crackers take their working position in the grooves of the stem.
7. Lubricate the compensators with clean engine oil and insert them into their original positions.
8. Lubricate the journals of the shafts, insert the camshafts and rotate so that the locating pin for the intake shaft gear is in position "4 hours", and graduation - "8 ocloc'k".
WARNING: Do not interchange the intake and exhaust shafts.
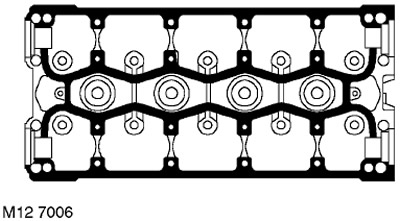
9. Apply continuous, thin bead of STC 4600 Sealant at the locations shown in the illustration. Spread the sealant in a thin layer over the surface with a roller trowel.
WARNING: Assembly of prepared parts must be done immediately to prevent contamination of surfaces with applied sealant.
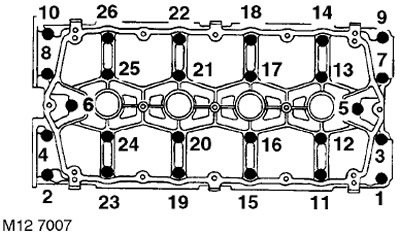
10. Install the camshaft cover and gradually, in the sequence shown in the figure, tighten the bolts to a torque of 10 Nm.
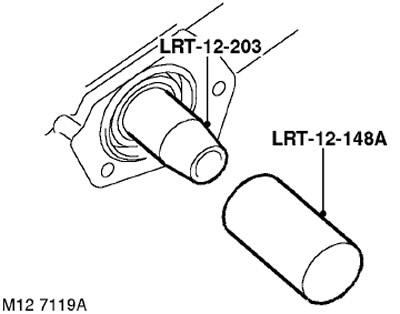
11. Bearing in mind that the front oil seals are black and the rear oil seals are red, install new oil seals using LRT-12-203 and LRT-12-148A.
CAUTION: The seals must be installed dry. Do not use tool LRT-12-148 to install oil seals.
12. Wipe gland covers and mating surfaces.
13. Establish a cover of a back epiploon of a final cam-shaft, screw in bolts and tighten them the moment of 25 Nanometers.
14. Establish a cover of a back epiploon of an inlet cam-shaft, screw in bolts and tighten them the moment of 6 Nanometers.
15. Adjust the gap between the electrodes in the candles by 1.00 mm.
16. Screw in the spark plugs and tighten them to 27 Nm.
17. Install a new elbow gasket on the cylinder head, install the elbow and tighten the bolts to 9 Nm.
18. Clean the intake manifold and mating surfaces on the cylinder head.
19. Install a new gasket on the head, a new intake manifold gasket, install the intake manifold, screw in the bolts and tighten them to a torque of 17 Nm.
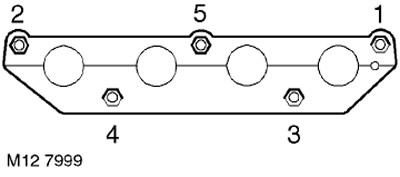
20. Wipe the exhaust manifold and mating surface on the cylinder head.
21. Having installed a new gasket, install the exhaust manifold, fit the nuts and tighten them to a torque of 45 Nm in the sequence shown in the figure.
22. Install the cylinder head.
ENGINE - MODIFICATION K, volume 1.8, Piston group, Cylinder head gasket.
Comments on this article