The location of the components of the exhaust gas recirculation system
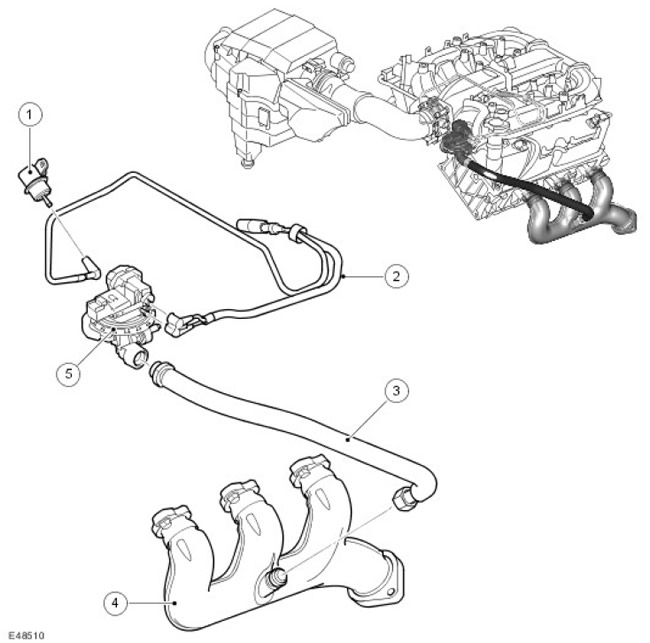
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | fuel rail damper |
| 2 | - | Vacuum regulation hoses |
| 3 | - | The pipeline connecting the exhaust manifold to the exhaust gas recirculation hose (EGR) |
| 4 | - | An exhaust manifold |
| 5 | - | ESM valve |
The toxicity of exhaust gases in a V6 gasoline engine is regulated by the engine control unit (ECM). The composition of the system for reducing the toxicity of exhaust gases includes:
- EGR system
- Crankcase emission reduction system
EGR system
ESM valve
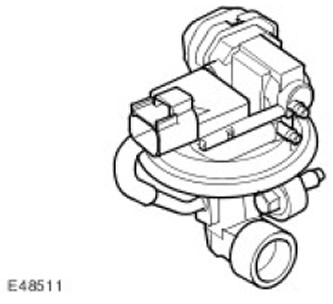
EGR control unit valve (ESM) located on the intake manifold and connected by a tube to the exhaust manifold. The sensor is connected to the wiring harness via a 6-pin connector. The ESM valve is controlled by an electric actuator using pulse-width modulation signals (PWM). The ESM valve allows the exhaust gases to be recirculated and returned to the engine. Since the exhaust gases contain very little free oxygen, they are practically inert. The exhaust gases replace the air in the cylinder, which lowers the combustion temperature. Reducing the combustion temperature leads to a decrease in the formation of nitrogen oxides (NOx).
The ESM valve incorporates an electronic differential pressure/manifold absolute pressure feedback transmitter (DPFE/MAP). The pressure sensor monitors the pressure difference across the diaphragm in the ESM system channel and transmits this data to the ECM. The differential pressure measured across the orifice is used to estimate the EGR flow rate. Electronic vacuum regulator (EVR) adjusts the vacuum signal to the ESM valve based on the electrical signal from the ECM. The ECM monitors the ESM level using feedback from the DPFE/MAP sensor. As a result, a closed control system is formed.
Engine ventilation system
The location of the components of the crankcase ventilation system
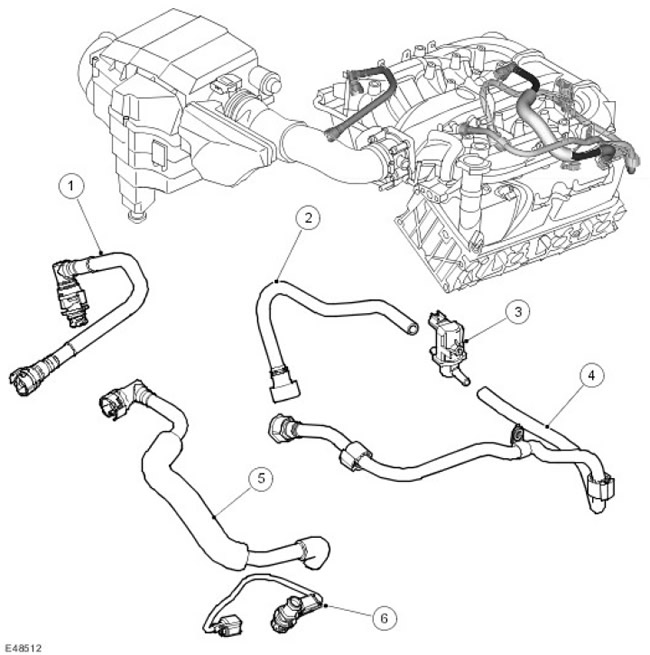
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | crankcase breather hose (CCV) and cam connector |
| 2 | - | Pipe connecting the evaporative emission system to the engine |
| 3 | - | Evaporative emission valve |
| 4 | - | crankcase breather hose (CCV) |
| 5 | - | Crankcase breather hose (PCV) and PCV valve |
| 6 | - | PCV connection cable with built-in thermistor |
Positive crankcase ventilation valve (PCV)
The composition of the forced crankcase ventilation system includes:
- Positive crankcase ventilation valve (PCV)
- Crankcase breather hose (PCV)
- crankcase breather hose (CCV)
Comments on this article