Vehicles with manual transmission without fuel-fired auxiliary heater (FBH)
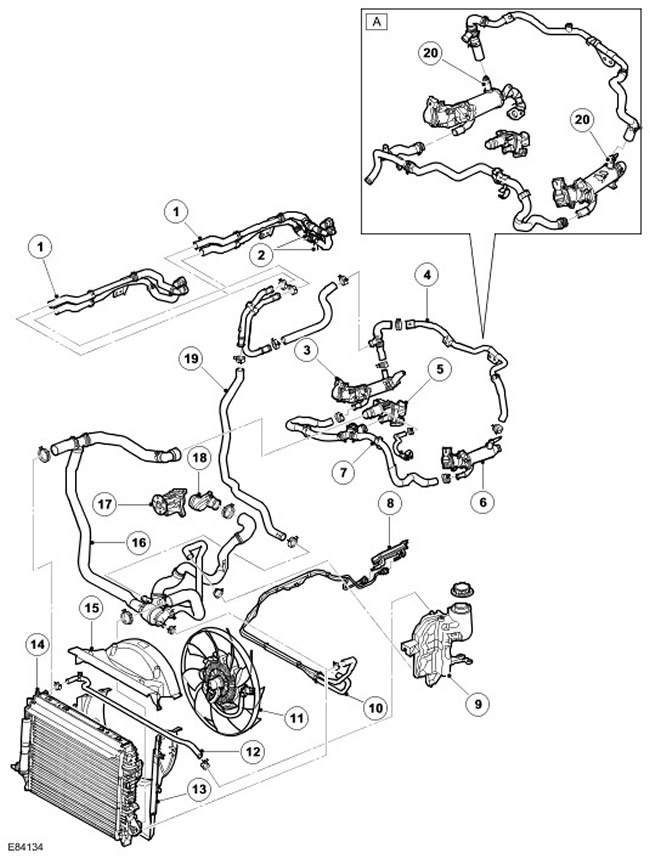
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| A | - | From model year 2007 |
| 1 | - | Heater hoses, inlet and outlet |
| 2 | - | Heater hoses, inlet and outlet, for vehicles with rear heater (installed additionally) |
| 3 | - | EGR valve |
| 4 | - | EGR valve hose |
| 5 | - | Outlet pipe assembly |
| 6 | - | EGR valve |
| 7 | - | EGR valve inlet hose |
| 8 | - | fuel cooler |
| 9 | - | Expansion tank |
| 10 | - | fuel cooler hose |
| 11 | - | Cooling Fan |
| 12 | - | Hose connecting radiator to expansion tank |
| 13 | - | Bottom casing |
| 14 | - | Radiator |
| 15 | - | Top casing |
| 16 | - | Hose with thermostat assy |
| 17 | - | Water pump |
| 18 | - | Inlet connector |
| 19 | - | Hose connecting heater to thermostat |
| 20 | EGR thermostat, 2 pcs. (from model year 2007) |
Vehicles with manual transmission and FBH
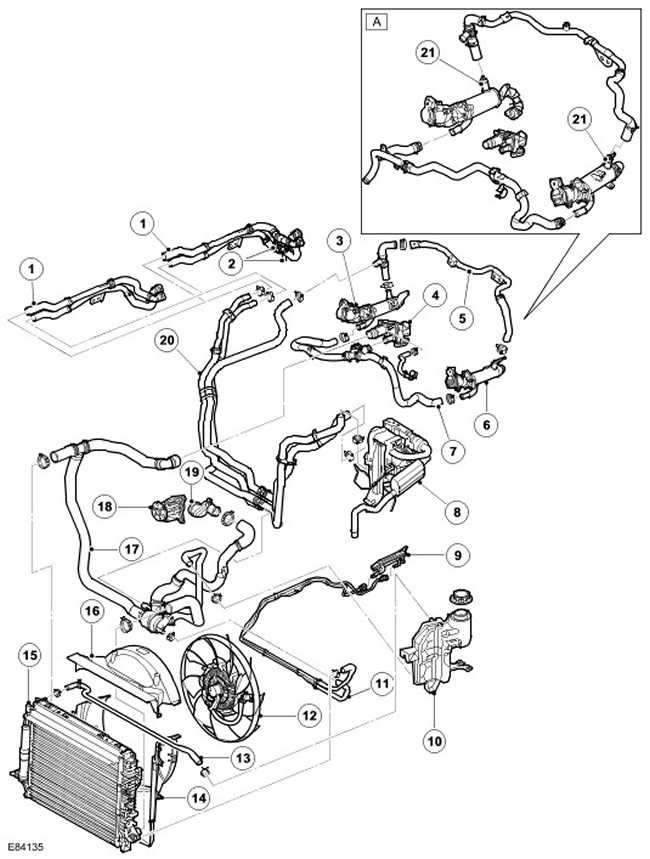
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| A | - | From model year 2007 |
| 1 | - | Heater hoses, inlet and outlet |
| 2 | - | Connections for rear heater (installed additionally) |
| 3 | - | EGR valve |
| 4 | - | Outlet pipe assembly |
| 5 | - | EGR valve hose |
| 6 | - | EGR valve |
| 7 | - | EGR valve inlet hose |
| 8 | - | FBH |
| 9 | - | fuel cooler |
| 10 | - | Expansion tank |
| 11 | - | fuel cooler hose |
| 12 | - | Cooling Fan |
| 13 | - | Hose connecting radiator to expansion tank |
| 14 | - | Bottom casing |
| 15 | - | Radiator |
| 16 | - | Top casing |
| 17 | - | Hose with thermostat assy |
| 18 | - | Water pump |
| 19 | - | Inlet connector |
| 20 | - | FBH hoses, inlet and outlet |
| 21 | EGR thermostat, 2 pcs. (from model year 2007) |
Vehicles with automatic transmission without FBH
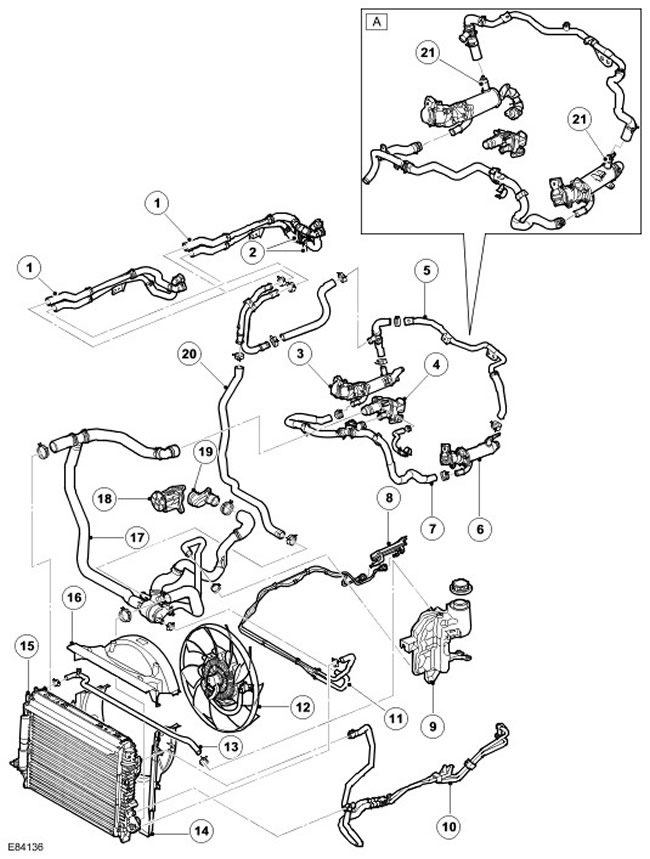
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| A | - | From model year 2007 |
| 1 | - | Heater hoses, inlet and outlet |
| 2 | - | Connections for rear heater (installed additionally) |
| 3 | - | EGR valve |
| 4 | - | Outlet pipe assembly |
| 5 | - | EGR valve hose |
| 6 | - | EGR valve |
| 7 | - | EGR valve inlet hose |
| 8 | - | fuel cooler |
| 9 | - | Expansion tank |
| 10 | - | Transmission Fluid Cooler Lines |
| 11 | - | fuel cooler hose |
| 12 | - | Cooling Fan |
| 13 | - | Hose connecting radiator to expansion tank |
| 14 | - | Bottom casing |
| 15 | - | Radiator |
| 16 | - | Top casing |
| 17 | - | Hose with thermostat assy |
| 18 | - | Water pump |
| 19 | - | Inlet connector |
| 20 | - | Hose connecting heater to thermostat |
| 21 | EGR thermostat, 2 pcs. (from model year 2007) |
Vehicles with automatic transmission and FBH
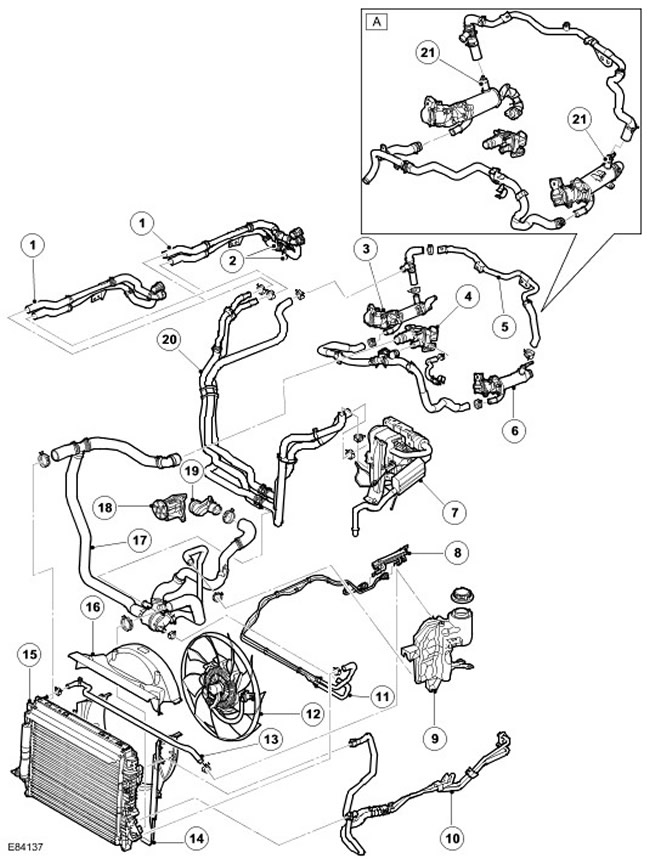
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| A | - | From model year 2007 |
| 1 | - | Heater hoses, inlet and outlet |
| 2 | - | Connections for rear heater (installed additionally) |
| 3 | - | EGR valve |
| 4 | - | Outlet pipe assembly |
| 5 | - | EGR valve hose |
| 6 | - | EGR valve |
| 7 | - | FBH |
| 8 | - | fuel cooler |
| 9 | - | Expansion tank |
| 10 | - | Transmission Fluid Cooler Lines |
| 11 | - | fuel cooler hose |
| 12 | - | Cooling Fan |
| 13 | - | Hose connecting radiator to expansion tank |
| 14 | - | Bottom casing |
| 15 | - | Radiator |
| 16 | - | Top casing |
| 17 | - | Hose with thermostat assy |
| 18 | - | Water pump |
| 19 | - | Inlet connector |
| 20 | - | FBH hoses, inlet and outlet |
| 21 | - | EGR thermostat, 2 pcs. (from model year 2007) |
General information
A bypass-type cooling system is used, which circulates the coolant through the engine and the heater circuit when the main thermostat valve is closed. The main purpose of the engine cooling system is to maintain the optimum temperature of the engine when environmental conditions and engine operation change. Other functions of the cooling system include heating the vehicle interior and cooling the transmission fluid and engine oil.
The cooling system includes the following components:
- Radiator
- Intermediate heat exchanger
- Car interior heater core
- Two fuel coolers
- Two exhaust gas recirculation system coolers (EGR)
- Fuel fired heater (FBH) (depending on the supply market)
- coolant pump
- Pressure control thermostat (PRT)
- Expansion tank
- Fan with electro-viscous coupling
- Connecting hoses and pipelines
Engine cooling system
The coolant circulates through the system under the action of a centrifugal type pump installed in front of the engine and driven by an additional V-ribbed belt. The pump pumps coolant through the cylinder block and cylinder heads through a chamber located in the collapse of the cylinder block. Some coolant passes through the built-in fuel and engine oil coolers. After passing through the engine and oil coolers, the coolant returns to the thermostat housing through the bypass tube. The coolant also passes through the EGR coolers (EGR) to the heater core and returns to the engine at the side of the pressure control thermostat (PRT).
On FBH-equipped engines, the coolant passes through the EGR coolers (EGR) to FBH (no matter if it works), and then enters the core of the heater. The coolant then returns to the PRT from the engine side.
On vehicles from model year 2007, a thermostat is installed in each outlet of the EGR heat exchanger. These thermostats control the flow of coolant through the EGR heat exchangers, reducing engine emissions and improving engine/heater warm-up.
The PRT housing contains a conventional thermostat, which is located so that the temperature of its sensing element is determined by the flow of coolant from both the radiator and the bypass channel. As a result, the opening temperature of the thermostat may vary depending on the environmental conditions. The PRT also has a spring loaded valve that restricts the flow of liquid through the bypass. This means that the engine can temporarily run without fluid flowing through the bypass, which in turn improves the performance of the interior heater.
The horizontal flow radiator has an aluminum alloy core and a drain cock on the lower right side of the rear. The lower radiator mounts are located at the ends of the radiator tanks. The mounts have rubber bushings that sit on top of the car body rails. The upper part of the radiator is fastened with pins that are passed through rubber bushings mounted on the front bearing element (FEC) above the radiator.
The intermediate heat exchanger is attached to the bottom of the radiator with two pins that are attached to the radiator tank fittings.
The upper radiator hose is connected to the PRT thermostat by a bypass hose, and the lower hose is directly connected to the outlet of the thermostat housing.
The expansion tank is installed in front of the left suspension support cup in the engine compartment. The expansion tank receives an excess amount of working fluid from the cooling system when it expands due to heating and, conversely, when the engine cools down, it compensates for its amount with a decrease in volume. Also, air accumulated in the coolant is discharged through this tank.
Transmission Fluid Cooler (only for vehicles with automatic transmission) installed on the side of the cold tank of the radiator. It is located in the middle of the left radiator tank.
The liquid enters the second fuel cooler from the side of the cold tank of the radiator from the additional cooling section and returns to the pressure control thermostat housing from the side of the radiator.
On vehicles equipped with FBH, this assembly is installed in front of the left suspension support cup in the engine compartment. Coolant always flows through the FBH, whether it is running or not. The exhaust gases of the heater are discharged into the wheel arch of the left front wheel. For more information refer to Auxiliary Heater (412-02B Auxiliary Heating)
To create additional air flow through the core of the radiator, especially when the car is stationary, a fan with an electro-viscous clutch is used, located behind the radiator. This fan serves the engine cooling system and the air conditioner cooling system. This assembly works like a conventional viscous fan, but with an electronic viscous coupling drive. Electronic engine control unit (ECM) controls the fan speed by adjusting the degree of inclusion of the viscous coupling. The degree of activation of the viscous coupling by the control unit is determined based on the temperature of the coolant, the temperature of the air at the inlet and the environment and the temperature of the oil in the gearbox, as well as the pressure in the air conditioning system. The applied fan has left rotation.
The speed of the viscous fan is optimally controlled by the ECM to suit all operating conditions.
NOTE: If the electrical connectors are disconnected from the viscous fan, it will rotate at "Idling", which can cause the engine to overheat. In this case, the ECM will store the corresponding DTC in memory.
Comments on this article