Camshaft lobe lift height
1. Measure the diameter (1) and diameter (2) vernier caliper with vernier. The difference between these two values is the cam lift.
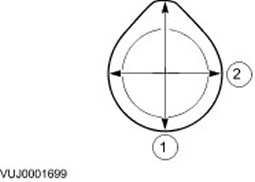
Deformation (warpage) mating surface of the cylinder head
1. Measure the misalignment of the block/cylinder head.
- Using a special tool, measure the degree of mismatch of the mating surfaces.
- If the value is out of specification, rework the mating surface.
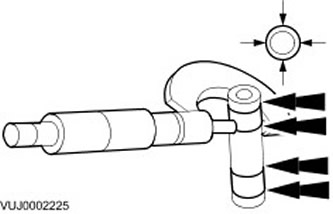
Piston pin diameter
1.
NOTE: Piston and piston pin form a single pair. Do not confuse these elements.
Measure the piston pin diameter.
- Measure in two directions
- If the values are out of specification, install a new piston and a new piston pin.
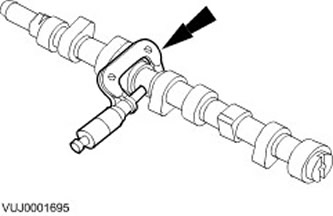
Camshaft journal diameter
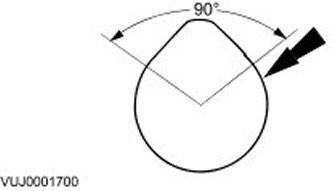
1. Determine the diameters of the camshaft journals
- To determine if the journals are out-of-round, measure the diameter at 90 degree intervals using a micrometer.
- To determine if there is a taper, measure the diameter of each journal at two locations offset along the axis of the journal.
- If the measurements are not correct, install a new camshaft.
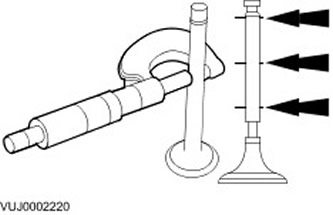
Valve stem diameter
1. Measure the diameter of the valve stems with a micrometer. If the measurement result is not correct, install a new valve.
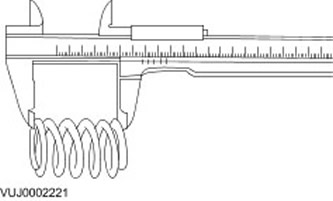
Valve spring free length
1. Using a vernier caliper, measure the free length of each valve spring. Make sure the value you get is correct.
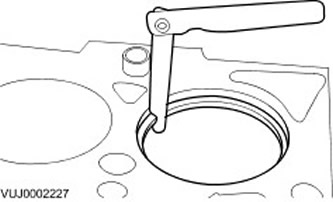
Piston ring gap
1.
CAUTION: Do not confuse piston rings. Piston rings should be installed in the same position and in the same places.
Using a feeler gauge, measure the piston ring clearance. The values given in the specification refer to the calibration ring used in the production of piston rings.
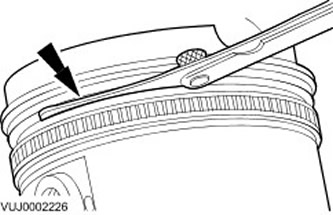
Gap between groove and piston ring
1.
NOTE: The piston ring must protrude from the piston groove. To determine the height clearance between the groove and the ring, insert a feeler gauge straight into the groove behind the ring.
Use a feeler gauge to measure the height clearance between the groove and the piston ring.
Axial clearance of the crankshaft
1. Using a dial indicator with brackets, measure the end play.
- The crankshaft end play is measured by lifting the crankshaft with a lever.
- If the measured value is outside the specified limits, install new thrust washers to compensate for backlash and repeat the measurement.
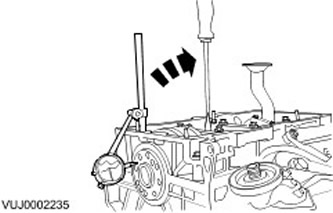
Camshaft axial clearance
1.
NOTE: Make sure the camshaft type is correct (specification).
Use a special tool to measure the axial clearance.
- Move the camshaft in both directions. Take readings and record the maximum and minimum value of the dial indicator. The axial clearance is equal to the difference between the maximum and minimum value.
- If the measurement result is out of specification, install new parts.
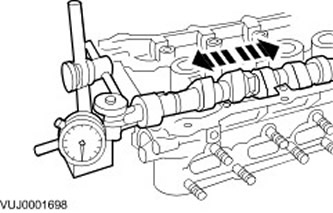
Inspection of the surface of the camshaft
1. Inspect the running surfaces of the camshaft lobes for pitting or damage. Minor pitting off the work surface is acceptable.
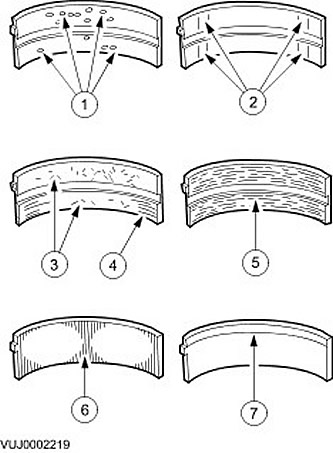
Bearing inspection
Inspect the bearings for the following defects.
- 1. Chipping (well formation) - fatigue wear.
- 2. Polished in places - incorrect fit.
- 3. Embedded particles - contaminated engine oil.
- 4. Scratches - contaminated engine oil.
- 5. Seizures - poor lubrication.
- 6. Wear on both edges - neck damage.
- 7. One lip wear - neck taper or improper fit.
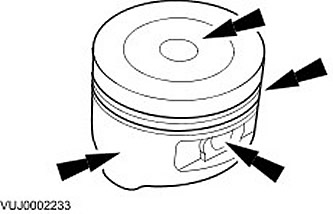
Piston Inspection
CAUTION: Do not use aggressive cleaning fluid or a wire brush to clean the piston.
Perform a visual inspection.
- Clean the piston skirt, piston pin bushing, grooves and piston head and inspect them for wear and cracks.
- If there are signs of wear on the piston skirt, check that the connecting rod is not deformed or twisted.
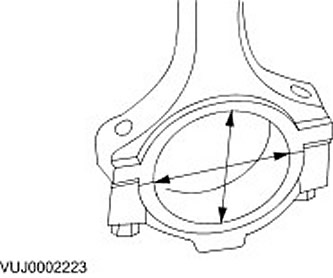
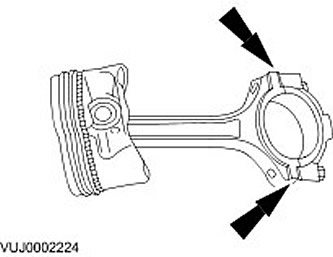
Connecting rod hole
1. Measure the connecting rod head bore in both directions. The measurement difference is the deviation of the connecting rod head hole from roundness (ovality). Check that the roundness deviation is correct.
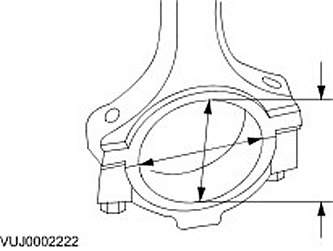
2. Measure the connecting rod head bore diameter in both directions. Make sure the connecting rod head bore diameter is correct.
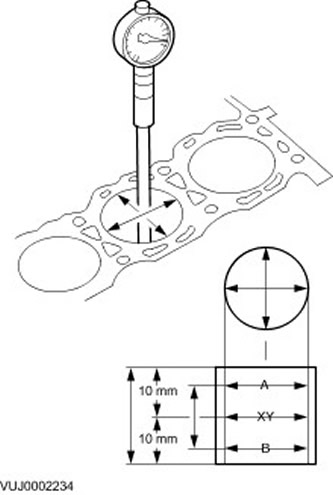
Deviation of the shape of the cylinder bore from roundness
1.
NOTE: The main bearing caps must be in place and must be tightened to the specified torque. However, bearing shells must not be installed.
Measure the bore diameter of the cylinder with an inside micrometer.
- To determine if there is any deviation in the shape of the cylinder from roundness or taper, take measurements in different directions and at different heights.
- If the measurement is not correct, honing the cylinder block or install a new cylinder block.
Cleaning and inspection of the exhaust manifold
1. Inspect the exhaust manifold flanges that mate to the cylinder head for signs of exhaust gas leakage.
2. Inspect the exhaust manifold for cracks, damage to gasket surfaces, or other damage that could render the manifold unusable.
Connecting rod cleaning
CAUTION: To avoid damaging the connecting rods, do not use a caustic cleaner solution.
Mark and separate the connecting rod into its component parts and clean them with solvent. Clean the lubrication channels.
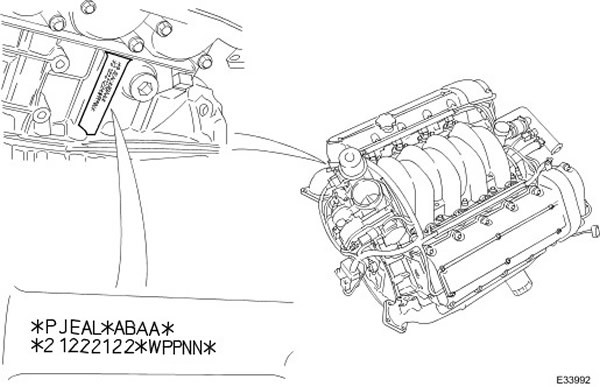
Radial clearance in the crankshaft main journal
CAUTION: These procedures should not be performed during the manufacturer's warranty period.
1.
NOTE: Example - *PJEAL* - Crankshaft journal diameter.
Read the class letters in the direction LEFT TO RIGHT = FRONT to REAR of the engine. For example, on this engine, the crankshaft journal at the front of the engine is a P and at the rear of the engine is an L. The selection of main bearing shells is described in the following table.
2.
NOTE: Example - *ABAA* - Crankpin Diameter (connecting rod bearing).
NOTE: For vehicles built prior to model year 2002.
NOTE: If the crankshaft main bearing housing bolts have been punched, they must be discarded and new bolts installed.
Read the class letters in the direction LEFT TO RIGHT = FRONT to REAR of the engine. For example, on this engine, the crankpin at the front of the engine is the letter A, and at the rear of the engine is also the letter A.
- Class A = 56.000 - 55.994 mm (bearing shell color code - blue).
- Class B = 55.994 - 55.988 mm (bearing shell color code - green).
- Class C = 55.988 - 55.982 mm (bearing shell color code - yellow).
3.
NOTE: Example - *ABAA* - Crankpin Diameter (connecting rod bearing).
NOTE: For vehicles manufactured from model year 2002.
NOTE: If the crankshaft main bearing housing bolts have been punched, they must be discarded and new bolts installed.
Read the class letters in the direction LEFT TO RIGHT = FRONT to REAR of the engine. For example, on this engine, the crankpin at the front of the engine is the letter A, and at the rear of the engine is also the letter A.
- Class A = 53.000 - 52.994 mm (bearing shell color code - blue).
- Class B = 52.994 - 52.988 mm (bearing shell color code - green).
- Class C = 52.988 - 52.982 mm (bearing shell color code - yellow).
4.
NOTE: Example - *21222122* - Cylinder and piston.
The cylinder diameter class is read from LEFT to RIGHT as follows:
- Bank 2 - cylinder 1, Bank 2 - cylinder 2, Bank 2 - cylinder 3, Bank 2 - cylinder 4, Bank 1 - cylinder 4.
- Bank 1 - cylinder 3, bank 1 - cylinder 2, bank 1 - cylinder 1.
- (Please note that in earlier publications, bank 1 was referred to as bank A and bank 2 as bank B)
- Class 1 cylinder diameter = 85.990 - 86.000 mm.
- Class 2 cylinder diameters = 86.000 - 86.010 mm.
- Class 3 cylinder diameters = 86.010 - 86.020 mm.
5.
NOTE: Example - *WPPNN* - Diameter of the crankshaft main bearing hole in the cylinder block
Read the class letters in the direction LEFT TO RIGHT = FRONT to REAR of the engine. For example, on this engine, the crankshaft journal at the front of the engine is a W and at the rear of the engine is an N. The choice of main bearing shells is described in the following table. JOIN DIAMETER AND MAIN BEARING HOLE.
6. NECK DIAMETER AND MAIN BEARING HOLE
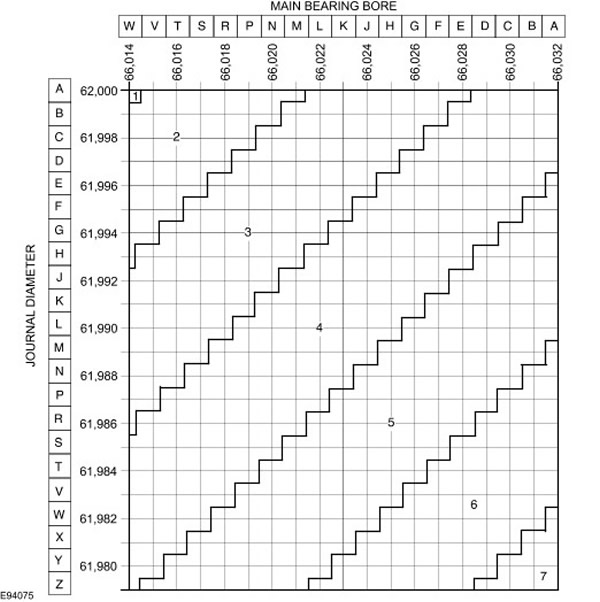
7.
NOTE: THIS PROCEDURE SHOULD BE PERFORMED ONLY WHEN REPLACING MAIN BEARING SHELLS
NOTE: Refer to the MAIN BEARING JOURNAL DIAMETER AND MAIN BEARING BOLE table in step 6 for tolerances and bearing information.
The number in each diagonal stripe indicates the PAIR of color-coded main bearing shells to be used on a particular journal, depending on the combination of journal diameter and bore diameter. The color codes for each band are as follows:
- Blue/Green and Blue/Green
- Blue/Green/Blue
- Blue and blue
- Blue and green
- green and green
- Green and yellow
- yellow and yellow
- Consider the crankshaft journal 5 (from the example class marking on the cylinder block) - the hole in the cylinder block is class N and the diameter of the crankshaft journal is class L. From this table it will be seen that the intersection point is in band 4, which corresponds to one blue liner and one green liner.
- When the correct pair of color codes for the neck is selected, one or another color liner can be installed on the cylinder block or on the base plate, but the liner to be installed on the cylinder block must have an oil groove, and the liner for the base plate must have a regular, even construction.
8.
NOTE: THIS PROCEDURE SHOULD BE PERFORMED ONLY WHEN REPLACING THE CRANKSHAFT OR CYLINDER BLOCK.
NOTE: Refer to the MAIN BEARING JOURNAL DIAMETER AND MAIN BEARING BOLE table in step 6 for tolerances and bearing information.
The thickness class for all main bearing shells must be selected to give a total radial clearance of not less than 0.022 mm and not more than 0.040 mm.
- The bore diameter for each bearing in the cylinder block/baseplate should be measured at two mutually perpendicular locations at an angle of 45°to the vertical at the center of the bearing.
- The smallest diameter of the two should be used.
- The diameter of each crankshaft main journal should be measured dynamically at a point corresponding to the middle of each bearing.
- When the correct pair of color codes for the neck is selected, one or another color liner can be installed on the cylinder block or on the base plate, but the liner to be installed on the cylinder block must have an oil groove, and the liner for the base plate must have a regular, even construction.
Radial clearance in the camshaft journal
1.
NOTE: Follow the prescribed procedure exactly. To perform the following measurements, the valve lifters must be removed.
NOTE: Make sure the camshaft type is correct (specification).
NOTE: Bearing caps and camshaft journals must be clean and free of oil.
Lay a piece of Plastigage clearance gauge thread on the bearing cap.
- Install the camshaft in the cylinder head without lubricating it.
- Lay a Plastigage clearance gauge thread equal in length to the width of the bearing cap on the corresponding journal.
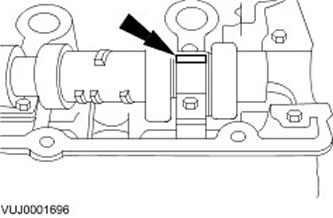
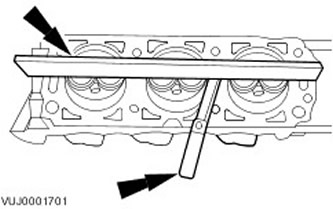
2. Install the camshaft bearing caps. Tighten the fastener in the sequence shown.
3.
NOTE: Do not knock on bearing caps.
Remove the camshaft bearing caps. Loosen the fastener in the sequence shown.
4. Carry out the measurement with a special tool.
- Compare the width of the Plastigage thread with the appropriate scale.
- The scale reading corresponds to the radial clearance in the bearing.
- If readings are out of specification, install a new camshaft.
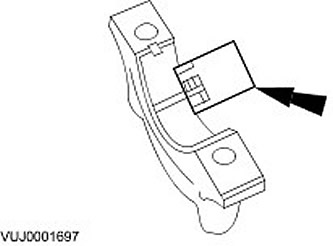
Correspondence of the piston pin and the bore in the piston
1.
NOTE: Piston and piston pin form a single pair. Do not confuse these elements.
Measure the diameter of the piston pin bore.
- Measure in two directions
- If the values are out of specification, install a new piston and a new piston pin.
Comments on this article