The location of the components of the electronic engine control system
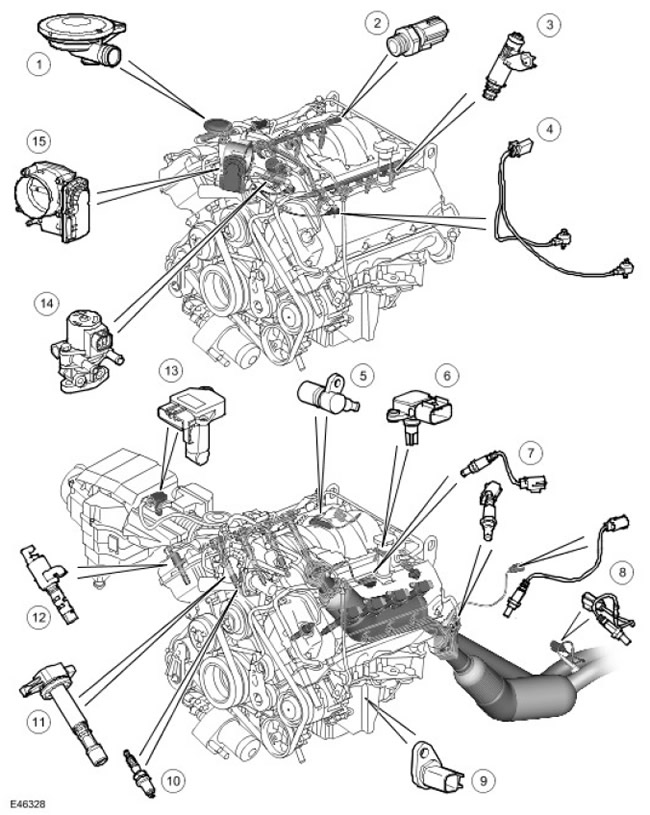
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | PCV (forced crankcase ventilation system) , |
| 2 | - | Fuel rail temperature sensor |
| 3 | - | Injectors |
| 4 | - | Knock sensor |
| 5 | - | CMP sensor (crankshaft position) |
| 6 | - | MAP sensor ( (manifold absolute pressure)) |
| 7 | - | Universal Heated Exhaust Oxygen Sensors (UHEGO) |
| 8 | - | Heated Exhaust Oxygen Sensors (HEGO) |
| 9 | - | CKP sensor (crankshaft position) |
| 10 | - | Spark plug |
| 11 | - | Ignition coils |
| 12 | - | Timing clutch control solenoid valve (VVT) |
| 13 | - | MAF sensor (mass air flow) |
| 14 | - | EGR valve (exhaust gas recirculation) |
| 15 | - | Electronic throttle |

| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | Power relay |
| 2 | - | Transfer box controller |
| 3 | - | ECM (the engine control unit) |
| 4 | - | APP (accelerator pedal position sensor) , |
| 5 | - | Stoplight switch |
| 6 | - | ABS control unit (anti-lock brakes) |
Diagram of input signals of the electronic control system
NOTE: A = wired

| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | Power relay |
| 2 | - | CMP sensor (crankshaft position) |
| 3 | - | CKP sensor (crankshaft position) |
| 4 | - | ECT sensor (coolant temperature) |
| 5 | - | APP sensor (accelerator pedal position sensor) |
| 6 | - | MAP ( (manifold absolute pressure)) |
| 7 | - | Engine oil temperature sensor |
| 8 | - | MAF sensor (mass air flow) /IAT (intake air temperature) |
| 9 | - | Fuel rail temperature sensor |
| 10 | - | RCM (airbag and seat belt control unit) |
| 11 | - | Stoplight switch |
| 12 | - | Clutch position sensor (not used) |
| 13 | - | knock sensors |
| 14 | - | ECM (the engine control unit) |
| 15 | Fuse 60P | |
| 16 | - | Fuse 25P |
| 17 | - | ignition switch |
| 18 | - | Fuse link 11 E |
NOTE: A = wired; D = CANCAN bus (local area network of controllers)
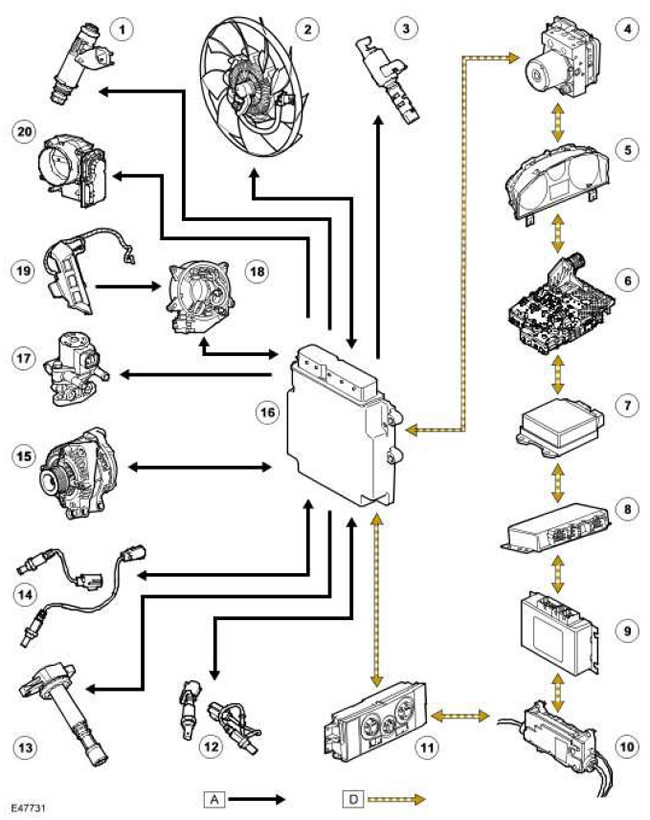
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | Injectors |
| 2 | - | Engine cooling fan. |
| 3 | - | Solenoid valves for controlling the clutches of the gas distribution mechanism (VVT) |
| 4 | - | ABS control unit (anti-lock braking system) |
| 5 | - | Dashboard |
| 6 | - | TCM (transmission control unit) , |
| 7 | - | RCM (airbag and seat belt control unit) |
| 8 | - | Differential controller |
| 9 | - | Transfer box controller |
| 10 | - | Parking brake controller |
| 11 | - | ATC control unit (automatic temperature control) |
| 12 | - | UHEGO (universal heated oxygen sensor) |
| 13 | - | Ignition coils |
| 14 | - | HEGO (Heated oxygen sensor) |
| 15 | - | Generator |
| 16 | - | ECM (the engine control unit) |
| 17 | - | EGR valve (exhaust gas recirculation) |
| 18 | - | coil spring |
| 19 | - | Cruise Control Switches |
| 20 | - | Electronic throttle |
General provisions
4.4 liter V8 engine controlled by the ECM (the engine control unit) manufactured by DENSO. Engine management system (EMS) governs the following:
- Fuel supply to the engine.
- Distribution of ignition points.
- Closed-loop refueling.
- Detonation management.
- Idle adjustment
- Decrease in exhaust toxicity.
- OBD (on-board self-diagnosis system) ,
- Providing an interface with the anti-theft system
- Cruise control
ECM block (the engine control unit) controls the phased fuel supply to all engine cylinders. The engine uses an ignition system with separate ignition coils (8 coils), which are installed directly on the spark plugs. In order to maintain optimum engine operating conditions, the ECM (the engine control unit) detects knocking in each individual cylinder and suppresses it by adjusting the ignition timing on each cylinder.
ECM Management Strategy (the engine control unit) based on the amount of torque requested by the driver. The EMS uses various sensors to determine the amount of torque that an engine needs to produce. In addition, EMS uses the CAN bus (controller LAN) to communicate with other electronic units in order to obtain additional information (e.g. vehicle speed from the ABS controller (anti-lock braking system)). The EMS processes these signals and decides on the amount of torque to be generated. Achieving the required torque is carried out through the control of various actuators that provide air, fuel supply and ignition timing control (throttle valve, injectors, ignition coils, etc.).
Comments on this article