Electronic throttle
Electronic throttle
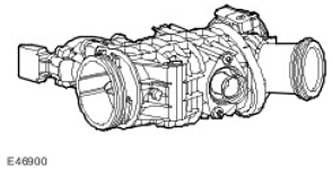
The electronic throttle controls the air flow into the engine. In addition to the normal engine power control functions, the electronic throttle performs functions such as cruise control, idle control and maximum engine speed limitation without additional hardware.
The electronic throttle assembly consists of a throttle body in which a throttle is installed, driven by a DC motor through a gearbox. The return spring moves the throttle towards the closed position.
The ECM controls the operation of the DC motor by sending two pulse-width modulation signals (PWM) to the exciting circuit of the H-shaped bridge in the electric motor. eCm changes the speed and direction of rotation of the motor by changing the duty cycle of the pulse width modulation signals.
To provide feedback control, the ECM senses throttle position using two Hall sensors in the throttle body. These sensors share a common 5V power supply and a common ground connection from the ECM and generate separate linear voltage signals proportional to throttle position that are sent to the ECM. The ECM uses the sensor 1 signal as the main throttle position signal, and the sensor 2 signal is used to check the validity of the first signal.
- Sensor 1 signal voltage can vary from 0.5 V (throttle valve fully closed) up to 4.5 V (throttle valve fully open).
- Sensor 2 signal voltage can vary from 4.5 V (throttle valve fully closed) up to 0.5 V (throttle valve fully open).
- Stores the appropriate fault code in memory.
- Turns on the SERVICE ENGINE warning light on the instrument panel.
- Depending on the nature of the malfunction, it enters emergency throttle control mode or stops damper control.
- If one sensor or throttle position controller in the ECM is faulty, then the ECM limits vehicle acceleration by limiting the throttle angle.
- If both sensors are faulty, the ECM cuts off fuel delivery, limiting engine speed to 1300 rpm.
Connector pins C0272 electronic throttle
| contact no | Description | Input signal / output signal |
| 1 | Supply voltage | Input signal |
| 2 | Throttle position | Output signal |
| 3 | Throttle position (+) | Input signal |
| 4 | Throttle position (-) | Input signal |
| 5 | normally closed | - |
| 6 | Signal mass | - |
Accelerator pedal position sensor
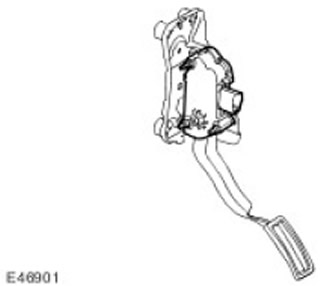
Accelerator pedal position sensor (APP) is an integral part of the accelerator pedal assembly.
The APP sensor allows the ECM to determine the throttle position requested by the driver via the accelerator pedal.
The APP sensor is located in the pedal box and consists of a two-track potentiometer, the sliders of which are connected to the accelerator pedal by means of rods. Each potentiometer track is supplied with 5V power and a ground connection from the ECM. The potentiometer generates a linear voltage signal proportional to the position of the accelerator pedal and sends it to the ECM. The signal voltage from track 1 of the potentiometer is about twice the voltage from track 2.
From the sensor signals, the ECM determines the driver's request as a percentage of pedal travel, where 0% is pedal released and 100% is pedal fully depressed. The driver's request is then used to calculate the throttle angle, fuel amount, and ignition timing. In addition, the ECM transmits a driver request via CAN for use by the transmission and brake control systems.
The ECM remembers the signal values corresponding to the fully closed and fully open positions and adopts new values in order to compensate for the replacement or wear of parts or assemblies.
The ECM constantly monitors the APP sensor signals for shorts, open, and plausibility. If an ECM malfunction is detected:
- Stores the appropriate fault code in memory.
- Turns on the SERVICE ENGINE warning light on the instrument panel.
- Disables transmission of driver requests via the CAN bus, which disables the downhill stability control function of the ABS modulator and reduces the performance of the automatic transmission (shifts more abruptly and the downshift function is disabled).
- Goes into emergency throttle control mode.
- If a fault is detected in only one track of the potentiometer, the ECM limits the vehicle's acceleration by limiting the throttle angle.
- If a fault is detected in both tracks of the potentiometer, the ECM will throttle the engine to maintain the engine speed at 1472 rpm with the brake pedal released and at 750 rpm (idling) - when the brake pedal is depressed or when the brake light switch fails.
- If a malfunction is detected in the ECM, the ECM cuts off the fuel supply, limiting the engine speed to 1300 rpm, or cuts off fuel injection to stop the engine.
Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor Connector Pin Chart
| contact no | Description | Input signal / output signal |
| 1 | APP sensor weight 1 | - |
| 2 | APP signal 1 | Output signal |
| 3 | APP sensor weight 2 | - |
| 4 | normally closed | - |
| 5 | APP signal 2 | Output signal |
| 6 | Reference voltage of APP sensor 2 | Input signal |
| 7 | Reference voltage of APP sensor 1 | Input signal |
| 8 | normally closed | - |
Comments on this article