Depending on the vehicle equipment, one of three types of light switches can be installed.
NOTE: The picture shows a high end lighting switch
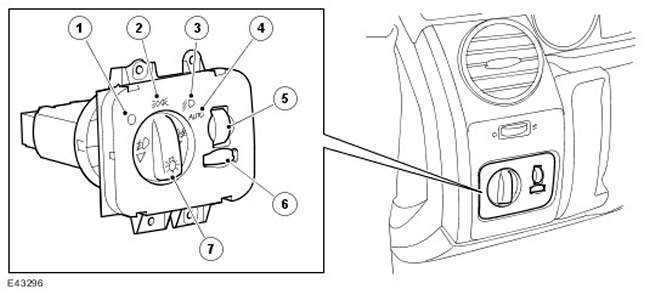
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | Off position (OFF) |
| 2 | - | Side lights included |
| 3 | - | Headlights on |
| 4 | - | Automatic headlight control enabled (if available) |
| 5 | - | Headlight range adjustment (if present, only for vehicles with coil spring suspension) |
| 6 | - | Dashboard dimming rheostat |
| 7 | - | rotary switch |
All light switch outputs except dimmer rheostat and headlight range adjustment outputs (if available), are expressed as a voltage drop across the switch of approximately 200 mV. Therefore, if an input voltage of 12 V is applied to the switch, then the output voltage is 11.8 V.
Rotary switch
The rotary switch can be set to one of four positions: OFF, parking lights, headlights and automatic mode (AUTO). On vehicles where there is no automatic mode, the switch has only three positions.
Three additional items available (extended switch) to control the fog lights: all fog lights are off, only the front fog lights are on, and the front and rear fog lights are on. If there are no fog lights, then there is only a position for turning on the rear fog lights.
On vehicles equipped with front fog lamps, they can only be turned on by pulling the switch when it is in the parking lamps or headlights on position.
On vehicles not equipped with front fog lights, only the rear fog lights can be turned on by pulling the switch when it is in the headlights on position.
The fog lights turn off automatically when the rotary switch is turned to the off position or when it is pressed to the fog light off position.
Manual headlight range adjustment (if available)
The manual headlight range control is only fitted to vehicles with coil spring suspension and is used to lower the headlights when there is a heavy load at the rear of the vehicle to change the orientation and tilt of the headlights.
For regulation, a rotary handwheel is used, connected to a rheostat, which gives various signals to the stepper motors for headlight range adjustment. Depending on the signal, the electric motors set the desired position of the headlights.
There are four marked positions on the control, from 0 to 3. The rotary knob can be moved to 8 positions to provide more precise headlight beam adjustment. The positions refer to the following vehicle load or driving conditions: Position 0 is the normal position for an unloaded vehicle. Positions 1-4 are used to compensate for a reduction in the height of the vehicle's rear suspension.
- 0 = Driver's seat only, or driver's and front passenger's seats occupied
- 0.5 = Driver, front passenger and third row seats occupied (for models with 7 seats) or all seats are occupied (for models with 5 seats)
- 1 = All seats occupied (for models with 7 seats)
- 1.5 = All seats occupied and maximum rear axle load
- 2 = Only driver's seat occupied and maximum rear axle load
- 3 and 4 = Can be used for certain driving conditions, such as off-road driving
Light brightness control
The brightness of the backlight of the instrument panel and other components of the control panel is controlled using pulse-width modulated signals. The dimming is done by turning a handwheel, which is connected to a rheostat and a switch in a high-level circuit.
A rheostat is a variable resistor that outputs high or low resistance depending on a given position. The rheostat voltage signal is sent to a switching capacitor or high level switch. The high level switch uses the voltage output of the rheostat to set the frequency at which the capacitor turns on, which generates 8-12V pulse-width modulated signals that determine the light level.
Comments on this article