Adaptive xenon headlight
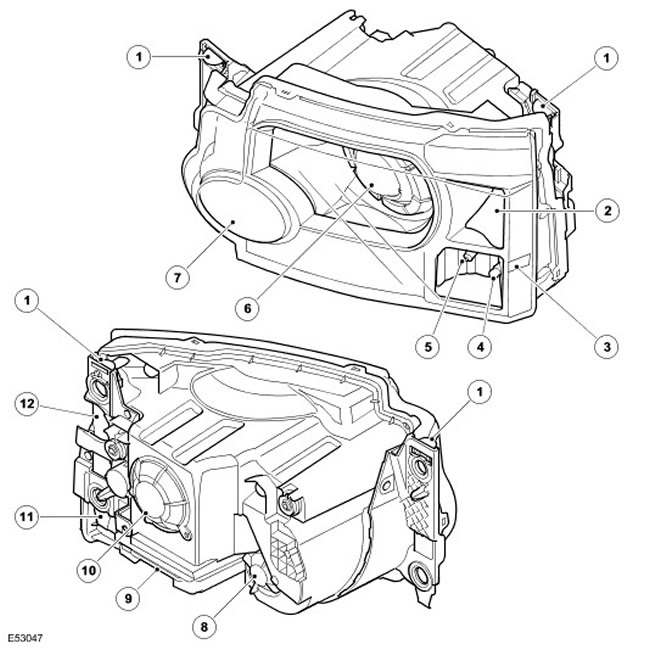
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | lock bar |
| 2 | - | Turn indicator |
| 3 | - | Side marker lamp (US only) |
| 4 | - | Marker lamp |
| 5 | - | Tilt side lights (excluding vehicles for the US market) |
| 6 | - | Adaptive xenon low/high beam headlight |
| 7 | - | Halogen high beam |
| 8 | - | Service hatch cover for high beam |
| 9 | - | xenon headlight controller |
| 10 | - | Service hatch cover for dipped/main beam headlights |
| 11 | - | Cover of the service hatch of a dimensional lantern and a lateral lantern with a deflected axis (not shown) |
| 12 | - | Turn signal service hatch cover (not shown) |
New adaptive headlamps are designed to improve visibility in various driving conditions. When cornering, the adaptive headlights improve illumination of the part of the road where you will continue to move. Optimization of the position of the light beam in the horizontal plane is performed automatically based on the position of the steering shaft and information from other sensors on the on-board system.
The adaptive headlamps are supplied with xenon lamps only and the system includes a dynamic headlight range adjustment circuit, which is described in section «Headlight range adjustment».
Inside the block headlight there is a module of a dual-mode xenon headlight, the position of which in the vertical and horizontal planes is regulated by the motor-reducer electric motor in accordance with the road profile and turning radius. Only the projector with dual-mode xenon headlights can change its position, while the main beam headlight with a halogen lamp remains stationary.
Adaptive headlights are controlled by their own controller, which is located at the bottom of the pillar «A», behind the CJB block. The controller adjusts the vertical and horizontal position of the xenon headlamp depending on the operation of the side tilt lamps, which is requested by the adaptive headlight unit controller, but controlled by the CJB unit.
How AFS works
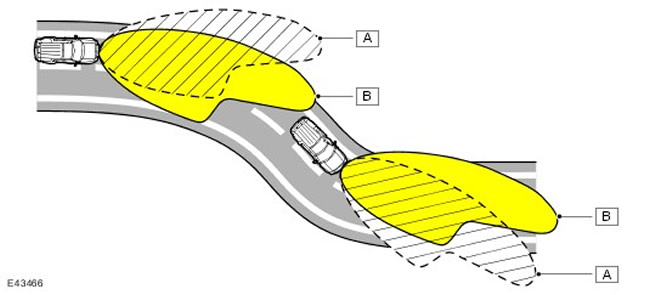
| A | Illumination distribution diagram for a conventional headlight |
| B | Light distribution diagram for adaptive headlights |
AFS controller
The AFS controller is a dual purpose device that also contains software for dynamic headlight range adjustment. The AFS controller is connected to the high-speed CAN bus and receives information from other on-board systems regarding the following parameters:
- Steering Angle - From Steering Angle Sensor
- Vehicle speed - from the ABS controller
- Low beam status - from instrument panel
- Suspension height - from the air suspension controller
- Odometer Reading - For Diagnostic Purposes Only
- Engine operation - from ECM
- Gear position - from transmission control unit or transfer case controller
- Engine cranking - from ECM
- Temperature outside / inside the cabin - for diagnostic purposes only
The AFS system will also be activated when the light switch is in the AUTo position and the AFS controller receives a signal to turn on the lights from the rain / light sensor and an engine confirmation signal.
The AFS controller then monitors input from other vehicle systems and controls the headlights according to the vehicle's speed and turning radius.
Connector pins C2193 AFS controller
| contact no | Description | Input signal / output signal |
| 1 | "Weight" | Input signal |
| 2 and 3 | Not used | - |
| 4 | High level CAN line | Input signal / output signal |
| 5 | CAN line low | Input signal / output signal |
| 6 | Signal of the gearmotor of the course drive of the right headlight | Output signal |
| 7 | Signal of the gearmotor of the course drive of the right headlight | Output signal |
| 8 | Not used | - |
| 9 | Right headlight tilt correction gearmotor 1 - "positive" (+) | Output signal |
| 10 | Right headlight tilt correction gearmotor 1 - "negative" (-) | Input signal |
| 11 | Electric motor of the gearmotor for correcting the tilt of the right headlight 2 - "positive" (+) | Output signal |
| 12 | Electric motor of the gearmotor for correcting the tilt of the right headlight 2 - "negative" (-) | Input signal |
| 13 | Powered by 12V ignition | Input signal |
| 14 to 17 | Not used | - |
| 18 | Signal of the gearmotor of the course drive of the left headlight | Output signal |
| 19 | Signal of the gearmotor of the course drive of the left headlight | Output signal |
| 20 | Not used | - |
| 21 | Electric motor of the gearmotor for correcting the inclination of the left headlight 1 - "positive" (+) | Output signal |
| 22 | Electric motor of the gearmotor for correcting the inclination of the left headlight 1 - "negative" (-) | Input signal |
| 23 | Electric motor of the gearmotor for correcting the inclination of the left headlight 2 - "positive" (+) | Output signal |
| 24 | Electric motor of the gearmotor for correcting the inclination of the left headlight 2 - "negative" (-) | Input signal |
Operating modes
The AFS system can operate in four modes:
- Maneuvering mode
- Normal driving mode
- High speed driving mode
- Reverse driving mode
The normal driving mode is used when driving at a speed of 30-70 km/h. In normal driving mode, both xenon headlights move in a ratio of 3:1, for example, during a left turn, the left headlight rotates 3 degrees, and the right one - 1 degree. In this mode, the maximum angle of rotation of the floodlight course drive in the direction of rotation is 12 degrees.
High speed driving mode is used when driving at speeds over 70 km/h. In high speed driving mode, both xenon headlights move in a ratio of 3:1, for example, during a left turn, the left headlight rotates 3 degrees and the right headlight rotates 1 degree. In this mode, the maximum angle of rotation of the floodlight course drive in the direction of rotation is 10 degrees.
In reverse mode, the headlights are deactivated when reverse gear is engaged. The headlights of the AFS system move to the center position, and the tilt side lights, if on, turn off. If the necessary conditions are met (those. vehicle speed exceeds 3 km/h), when reverse gear is disengaged, the AFS floodlights move to the position corresponding to the steering angle and the tilt side lights come on.
Adaptive xenon headlights
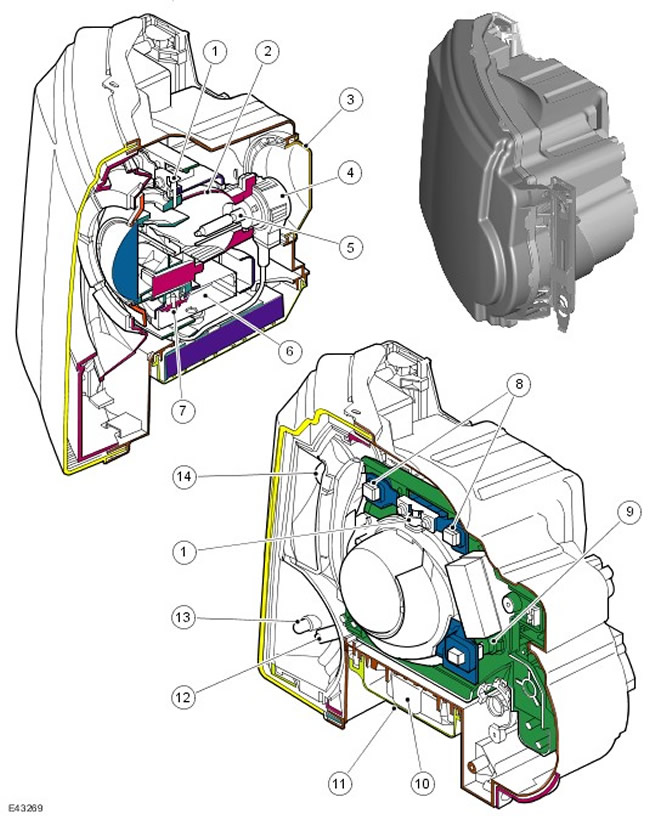
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | Spotlight Horizontal Axis |
| 2 | - | Reflector |
| 3 | - | Service hatch cover |
| 4 | - | Xenon lamp socket DS2 |
| 5 | - | Xenon lamp DS2 |
| 6 | - | Gearmotor of the course drive for adjusting the adaptive headlight horizontally |
| 7 | - | Horizontal gear motor drive |
| 8 | - | Vertical axes of the spotlight |
| 9 | - | Gearmotor of the course drive for adjusting the adaptive headlight vertically |
| 10 | - | xenon headlight controller |
| 11 | - | Controller cover |
| 12 | - | Tilt side lamp (excluding vehicles for the US market) |
| 13 | - | marker lamp |
| 14 | - | Turn signal lamp |
The design of the adaptive xenon headlight is similar to that of the non-adaptive xenon headlight. To perform the AFS function, a platform has been added to the block headlight device, on which AFS nodes are located. The rest of the lights included in the xenon block headlights do not differ from those described earlier. The operation of the pivoting side lamps on the adaptive headlight is different from the operation of the cornering lights when turning on a conventional xenon headlight.
The platform design has a radial bearing at the top and a thrust washer at the bottom that provide support points for the horizontal axis of the xenon floodlight. The end of the lower axle of the headlight has splines, which is inserted into the splined hole of the electric motor of the AFS gearmotor for vertical adjustment. The platform is suspended from two flexible supports at the top that provide attachment points for the vertical axis of the xenon spotlight, allowing the spotlight to be adjusted vertically. The lower part of the platform is attached to the electric motor of the AFS vertical adjustment gearmotor.
AFS geared motor motors are DC motors controlled by the AFS controller. The AFS controller also provides the motor ground circuit.
The gearmotors include a potentiometer, which is connected by wires to the gold-plated contacts of the connector connected to the AFS controller. Two wires connected to each gearmotor provide the AFS controller with feedback signals, which allows you to adjust the position of the xenon spotlight with high accuracy.
For dynamic headlight range adjustment, the AFS controller uses signals from the front and rear suspension and controls the electric motor of the geared motor in the vertical plane. In addition, the AFS controller adjusts the light range by changing the headlight range, for which the speed signal received from the ABS controller is used.
Initiation procedure
The procedure for initiating the system consists in bringing the axes of the headlights to the correct position in the vertical and horizontal planes and is carried out after the AFS controller receives a signal to turn on the ignition.
Initiation of the headlight range adjustment takes less than 3 seconds. Electric motors for headlight range adjustment from their original position (extreme top, extreme bottom or any intermediate) are brought to the lowest position and then to the horizontal position (axis tilt is 0 degrees).
Initiation of the AFS course drive starts less than 1 second after the headlamp leveling motor initiation, so that the vertical axis of the headlights is 0 degrees or less to avoid dazzling oncoming traffic. The initiation of the course drive of the headlights is completed in less than 2.5 seconds. The electric motors of the course drive motors of the right and left headlights first turn the headlights completely from the 0°position inward, then turn them completely outward, and then again set them to the 0°position.
Emergency mode
In the event of an error in the operation of the AFS system, a visual indicator is activated on the instrument panel to warn the driver of a malfunction. The signaling device turns on at position II of the key in the ignition lock and does not stop glowing until the malfunction is eliminated. The AFS warning light also comes on if the steering shaft position sensor is faulty or if there is no vehicle speed signal.
The activation of the AFS warning light is not necessarily related to a malfunction of this system. Another system may be faulty, on which the operation of the AFS system depends.
The AFS controller performs diagnostics with each system activation request. If an error is detected, the AFS controller suspends the system.
If the AFS system fails when the xenon headlight is not pointing straight ahead, the AFS controller will attempt to zero the xenon headlight (straight ahead). If this adjustment is not possible, the AFS controller will lower the floodlight using tilt correction motors to avoid dazzling oncoming vehicles.
The AFS controller software allows you to find your own internal faults. If it detects its own fault, the controller will set the headlights to zero and stop further control.
Fault codes can be scanned using the T4 scan tool.
Tilt side lights
NOTE: * US vehicles are not equipped with tilt side lights
Pivot side lights are designed to illuminate the direction of travel when turning at low speed. These lights are standard on vehicles with adaptive headlights. The design of diffusers allows deflecting the light beam by approximately 45 degrees from the vehicle axis. The tilt-axle side lights are controlled by the CJB unit.
A tiltable side lamp is built into the outer part of the headlamp and is located in the same housing as the reflector and the side marker lamp.
The tilt side light uses a 35W H8 halogen bulb inserted into a socket that is wired to a connector on the headlight housing. The cartridges are inserted into the hole in the headlight housing and rotated until they lock. The lamp can be accessed through a removable cover on the back of the headlight housing.
AFS headlight control
Pivot side light control is based on the steering wheel position sensor signal received by the AFS controller and the CJB. The AFS controller sends a request to turn on the side pivot light to the CJB, which turns on the light bulb.
When driving at speeds above 48 km/h, the tilt side lamp turns on in the direction the vehicle is turning when the steering wheel angle reaches 70 degrees. If the vehicle's turn decreases, the tilt side lamp turns off when the steering wheel angle reaches 50 degrees.
When driving at speeds below 48 km/h, the tilt side lamp turns on in the direction the vehicle is turning when the steering wheel angle reaches 245 degrees. If the vehicle's turn decreases, the tilt side lamp turns off when the steering wheel angle reaches 225 degrees.
The tilt-axle side lights are controlled by the CJB unit. After the lamp enters the operating mode, the CJB unit reduces its brightness by applying pulse-width modulated signals (PWM) for approximately two seconds. When the lamp turns off, the CJB dims the lamp by reducing the voltage of the PWM signals.
Comments on this article