Communication networks (multimedia bus MOST)
NOTE: D - high speed CAN bus, P - MOST
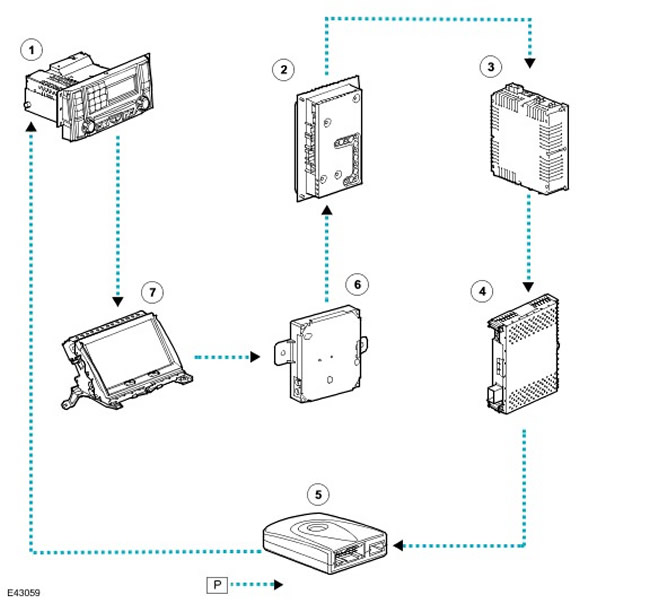
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | Dashboard |
| 2 | - | Amplifier Harman Kardon Logic 7 |
| 3 | - | Rear seat infotainment module |
| 4 | - | Automatic DVD changer |
| 5 | - | Amplifier Harman Kardon |
| 6 | - | Transceiver |
| 7 | - | Traffic channel (TMS) |
| 8 | - | Touch screen (TSD) |
| 9 | - | TV tuner |
| 10 | - | Unified audio headunit (IHU) |
Communication networks (CAN bus)
NOTE: D - high speed CAN bus, N - medium speed CAN bus, O - local LIN data bus
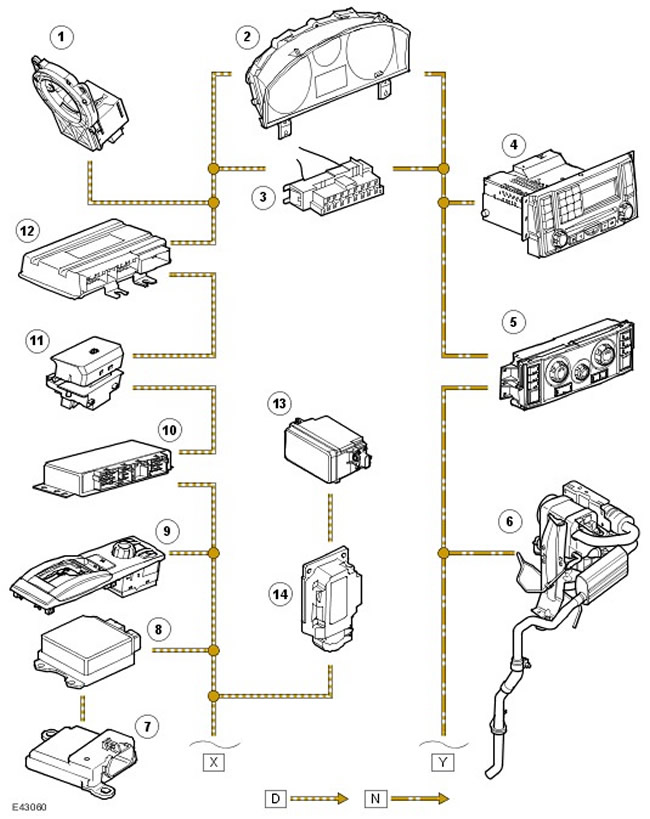
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | Steering angle sensor |
| 2 | - | Dashboard |
| 3 | - | Diagnostic connector |
| 4 | - | Unified audio headunit (IHU) or head unit |
| 5 | - | Control panel for heater and interior ventilation |
| 6 | - | Fuel fired heater |
| 7 | - | Passenger presence sensor (only for US market vehicles) |
| 8 | - | Passive safety controller |
| 9 | - | TERRAIN RESPONSE™ System Controller |
| 10 | - | Rear axle differential controller |
| 11 | - | Parking brake controller |
| 12 | - | Air suspension controller |
Communication networks (CAN bus)
NOTE: D - high speed CAN bus, N - medium speed CAN bus, O - local LIN data bus
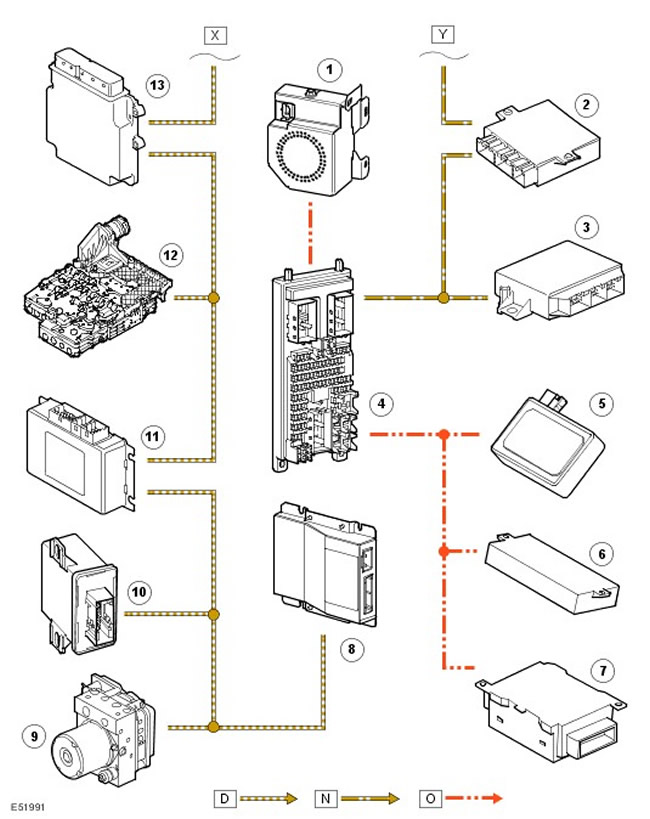
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | The engine control unit |
| 2 | - | Tire pressure monitoring system controller |
| 3 | - | Parking Assist Controller (PDC) |
| 4 | - | Central switching unit (CJB). |
| 5 | - | Rain sensor |
| 6 | - | Memory controller |
| 7 | - | Sunroof controller |
| 8 | - | Self-powered alarm siren (BBUS) |
| 9 | - | ABS controller |
| 10 | - | adaptive headlights (AFS) |
| 11 | - | Transfer box controller |
| 12 | - | Gearbox controller |
There are several types of data buses in the vehicle wiring, through which commands and other information are exchanged between electronic control units. The tire configuration depends on the model and equipment level of the particular vehicle.
The following are the types of multiplex avionics buses:
- High Speed Controller Network Bus (CAN)
- Medium speed CAN bus
- multimedia bus (MOST)
- Video interface (GVIF)
- Local LIN bus
- SLIN security system local bus
| Tire | Transfer rate | Protocol |
| High speed CAN bus | 500 kbps | 11898 |
| Medium speed CAN bus | 125 kbps | 11898 |
| MOST | 24 Mbps | MOST association |
| GVIF | 1.95 Gbps | Sony Original Design |
| LIN bus | 9.6 kbps | LIN Consortium |
Controller network (CAN)
The CAN bus is a high speed data link where ECUs automatically transmit information over the bus every few microseconds. The speed of information transfer on other buses is much lower. These tires are mainly responsive to «events», i.e. transmit messages only in response to ECU requests or when the status of switches and sensors changes.
Structurally, the CAN bus is two-wire, made in the form of the so-called «twisted pair», and all other buses are single-wire. Wiring can be repaired using crimp connections. The length of the unwound CAN bus must not exceed 40 mm.
The car uses two CAN buses:
- Medium speed tire
- high speed bus
- Unified audio headunit (IHU) or standard head unit
- Control panel for heater and interior ventilation
- Fuel fired heater
- Parking assistance
- Tire pressure monitoring system controller
- Central switching unit
- Steering angle sensor
- Air suspension
- Electric parking brake
- Rear axle differential controller
- TERRAIN RESPONSE™ System Controller
- Passive safety controller
- Electronic engine control unit
- Gearbox controller
- Adaptive Headlight Controller
- Anti-Lock Brake Controller (ABS)
Electronic blocks can be connected by a loop (CAN input/output) or with the help of branches from the main bus. In the first case, a controller failure leads to the failure of the entire network at a given point. In the second case, only the faulty controller fails, while the rest of the network remains operational.
Multimedia bus (MOST)
The MOST fiber optic bus is designed for data transmission within the infotainment system. The MOST fiber optic bus provides a daisy chain connection of devices, each of which has a MOST input and output connector.
MOST is a synchronous network. The network master sets the time, and all other devices operate according to the clock pulses of this timer. For the MOST network, the master unit is the integrated audio headunit (IHU).
The MOST network has the following features:
- ease of connections;
- reduced number of wires;
- support for synchronous and asynchronous data transfer protocols;
- Simultaneous support for up to 64 devices;
- high data transfer rate.
- The minimum tire bending radius is 25 mm.
- It is not recommended to look at the end face of a live bus connector.
- MOST tires cannot be repaired. To replace damaged tires, you can order «bypass» wiring.
Video interface (GVIF)
The GVIF bus is a development owned by Sony, designed to transmit video information from a transmitter to a display. In this case, it is only used to transmit video signals from the navigation computer to the touch screen (TSD).
Local LIN bus
The vehicle has two LAN buses (LIN). One of them connects the rain sensor, sunroof and seat memory to the central switching unit, and the second connects the BbUs (self-powered alarm siren) also with central switching unit.
The LIN bus configuration is based on the principle «Master/Slave» (those. there are master and slave devices in the network). The master device stores "schedule", i.e. a list of all LIN data frames or packets in order, sorted by time and number of sends in a given cycle. The master sends on the bus «headlines», which allow slaves to set their frame transmission order. The slave device then fills the space after the header with the contents of the frame. Frame IDs come from the LIN specification and are grouped by frame size in bytes. All nodes connected to the LIN bus are optional, therefore there is a different schedule for each reordering and switching of the master device between these devices depending on the data stored in the vehicle configuration file. The CJB also acts as a bi-directional gateway between the medium speed CAN bus and the LIN bus, enabling signal exchange between the two buses.
The bus is single wire and operates at 9.6 kbps. The data transfer protocol is defined by the LIN consortium.
Diagnostic connector
The diagnostic connector allows information to be transmitted between the vehicle's electronic components and the T4 diagnostic tool via high or medium speed CAN bus, as well as indirectly through the dashboard. The diagnostic connector is located in the lower part of the control panel trim on the driver's side, under the steering column.
Comments on this article