Location of elements
NOTE: The picture shows a car with RHD (left hand drive), vehicle with LHD (right hand drive) has a similar device.
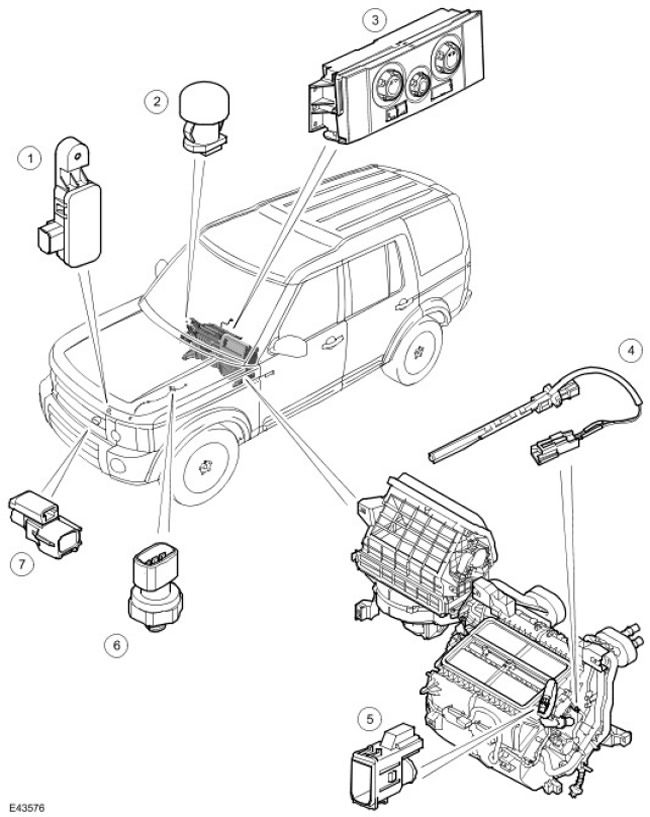
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | Dirt sensor (Japan only) |
| 2 | - | Solar radiation sensor |
| 3 | - | ATC controller (automatic temperature control) |
| 4 | - | Evaporator temperature sensor |
| 5 | - | Car interior temperature sensor, car interior temperature and humidity sensor (Japan only) |
| 6 | - | Refrigerant pressure sensor |
| 7 | - | Outdoor temperature sensor |
General information
The control system regulates the operation of the A/C system (conditioning) , heating and ventilation, maintaining the set air temperature and its distribution in the cabin.
The vehicle can be equipped with a manual or automatic control system. The manual control system maintains a constant temperature at the heater outlet for the right and left sides of the passenger compartment, but allows manual selection of the air intake source, fan speed and distribution of air in the passenger compartment. The automatic system automatically regulates the temperature, volume and distribution of the air leaving the heater, maintaining the individual temperature conditions set for the LH (left) and RH (right) sides of the salon. The automatic system also allows manual forced selection of the air intake source, fan speed and air distribution. Manual and automatic systems include the following components.
- ATC controller (automatic temperature control).
- Outdoor temperature sensor.
- Refrigerant pressure sensor.
- Evaporator temperature sensor.
- Cabin air temperature sensor.
- Solar radiation sensor.
- Pollution sensor.
- Air humidity sensor.
ATC module
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) installed in the center of the instrument panel. The integrated control panel contains push and turn switches to control the system. LED (LEDs) on the switches and next to the switches are lit to indicate the current system settings. In addition, when the headlights or position lamps are switched on, the switch symbols are illuminated.
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) processes input signals from control panel switches, system sensors and medium speed CAN bus (local area network of controllers) and issues proper control signals to the A/C system (air conditioning) , heating and ventilation. In addition to A/C system control (air conditioning) ATC controller (automatic temperature control) also manages the following devices:
- Front seat heaters. For more information contact Seats (501-10 Seating)
- Rear window heater. For more information refer to Glass, Frames and Mechanisms (501-11 Glass, Frames and Mechanisms)
- Windscreen heater. For more information refer to Glass, Frames and Mechanisms (50111 Glass, Frames and Mechanisms)
- Windshield washer jets and door mirror defrosters For more information, refer to Rear View Mirrors (501-09 Rear View Mirrors)
System control panel in manual mode
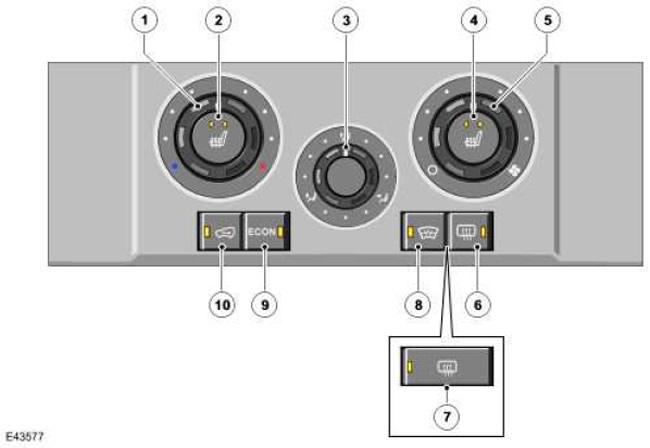
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | Thermal relay |
| 2 | - | Heating switch LH (left) front seat |
| 3 | - | Air distribution switch |
| 4 | - | Heating switch RH (right) front seat |
| 5 | - | Fan switch |
| 6 | - | Rear defroster switch (models with heated windshields) |
| 7 | - | Rear defroster switch (models without heated windshields) |
| 8 | - | Windshield defroster switch (if installed) |
| 9 | - | ECO switch |
| 10 | - | Air recirculation switch |
Automatic system control panel
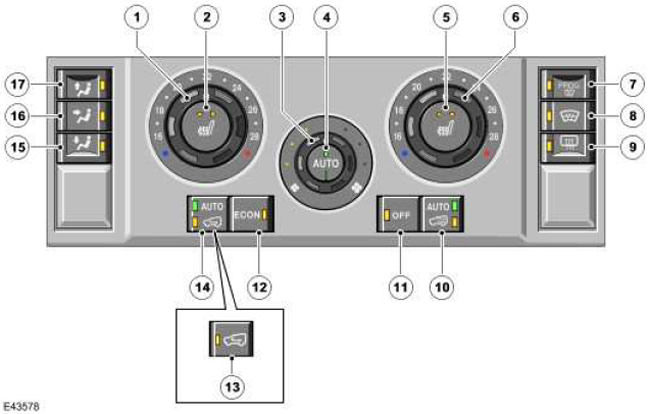
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | Temperature switch in LH (left) parts of the salon. |
| 2 | - | Heating switch LH (left) front seat |
| 3 | - | Fan switch |
| 4 | - | Auto Mode Switch |
| 5 | - | Heating switch RH (right) front seat |
| 6 | - | Temperature switch in RH (right) parts of the salon. |
| 7 | - | Switch for programmable defrost function |
| 8 | - | Heated windshield switch |
| 9 | - | Heated rear window switch |
| 10 | - | Switch for additional climate control system |
| 11 | - | System switch |
| 12 | - | ECO switch |
| 13 | - | Cabin air recirculation switch (models without pollution sensor) |
| 14 | - | Cabin air recirculation switch (models with pollution sensor) |
| 15 | - | Air distribution switch: at foot level |
| 16 | - | Air distribution switch: face level |
| 17 | - | Air distribution switch: windshield |
Input and output signals
Communication between ATC controller (automatic temperature control) and on-board electrical wiring is carried out through four electrical connectors. From the sensors of the control system, signals are sent via wired communication to the input of the ATC controller (automatic temperature control). In addition, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) uses the local LI N bus to communicate with the auxiliary climate control system, the damper motors in the heater module and the medium speed CAN bus (controller LAN) to communicate with other on-board control modules. For more information refer to Communications Network (418-00 Module Communications Network)
Outdoor temperature sensor
The outdoor temperature sensor is an NTC type thermistor (negative temperature coefficient) , which feeds to the input of the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) outdoor temperature signal. The sensor is mounted on a bracket located at the rear in the center of the bumper beam.
Refrigerant pressure sensor
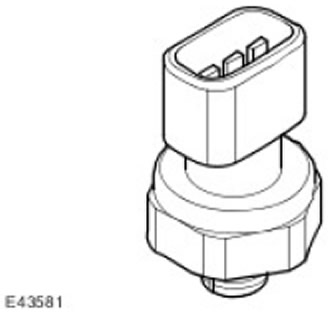
The refrigerant pressure sensor supplies to the input of the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) pressure signal in the high pressure line of the refrigerant circuit. The refrigerant pressure sensor is located in the refrigerant line between the condenser and the thermostatic expansion valve.
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) applies a 5 V reference to the refrigerant pressure sensor and receives a voltage feedback between 0 and 5 V corresponding to the system pressure.
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) uses the pressure signal from the refrigerant pressure sensor to protect the system from overpressurization and to calculate the load from the A/C system compressor (air conditioning) on the engine. ATC controller (automatic temperature control) also transmits load data from the A/C compressor (air conditioning) to the ECM (engine control module) via medium-speed CAN bus (controller LAN), as well as on the instrument panel and via the high-speed CAN bus (controller LAN). This information is used to control the engine cooling fan speed.
To protect the system from excessive pressure, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) Sets for A/C Compressor (air conditioning) lowest possible flow if pressure:
- decreases to 1.9±0.2 bar (27.5±3 psi2), ATC controller (automatic temperature control) restores the load on the compressor of the A/C system (air conditioning), when the pressure rises to 2.8±0.2 bar (40.5±3 psi2).
- increases to 33±1 bar (479±14.5 lb/in2), ATC controller (automatic temperature control) restores the load on the compressor of the A/C system (air conditioning), when the pressure decreases to 23.5±1 bar (341±14.5 psi2).
Evaporator temperature sensor
The evaporator temperature sensor is an NTC thermistor (negative temperature coefficient) , which transmits to the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) evaporator outlet temperature signal. The evaporator temperature sensor is installed on the right side of the heater housing.
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) sets the load on the A/C compressor based on the evaporator temperature sensor (air conditioning) and thus regulates the operating temperature in the evaporator.
Cabin air temperature sensor
The cabin air temperature sensor is an NTC thermistor (negative temperature coefficient) , installed behind the driver's side center console trim grille. The sensor is connected to a tube, the other end of which is connected to a diffuser located on the side of the heater block housing. The air coming from the heater and passing through the diffuser causes air to move through the tube, which leads to the intake of air from the passenger compartment through the grille, which passes through the temperature sensor.
Humidity sensor (if available)
Capacitive type humidity sensor built into the interior air temperature sensor (see above).
The sensitive element of the humidity sensor is a film capacitor on substrates of various materials. The dielectric separating the plates is made of a polymer that absorbs or evaporates moisture in proportion to the relative humidity of the air passing through the sensor, and the sensor capacitance changes. To protect against mechanical influences, the sensitive element is covered with a nylon mesh.
Cabin humidity and temperature sensors are connected to a printed circuit board located in the sensor housing. The printed circuit board is supplied with 5 V supply voltage from the ATC controller (automatic temperature control). From the printed circuit board, separate temperature and humidity signals are sent to the ATC controller (automatic temperature control).
Solar radiation sensor
The solar radiation sensor consists of two photocells, which are fed to the input of the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) light intensity signals, the first signal corresponds to the illumination on the left side of the car, and the second - on the right side. The signals are a measure of the intensity of the sun's heating of the car's interior and are used by the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) to control fan performance, temperature and air distribution to improve comfort. The sensor is installed in the central part of the front panel, on top. It is supplied with a 5 V supply voltage from the ATC controller (automatic temperature control).
Pollution sensor
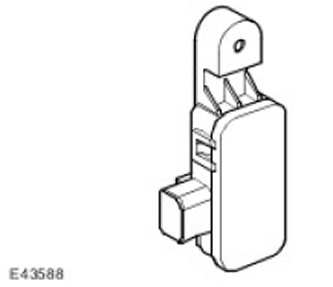
With pollution sensor ATC controller (automatic temperature control) controls the level of gaseous hydrocarbons and oxides (nitrous oxide, sulfur oxides and carbon monoxide). The sensor is mounted on a bracket, which is installed in the front part of the carrier at the upper left corner of the condenser.
The pollution sensor is supplied with power from the battery through the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) . The sensor provides separate signals on the content of gaseous hydrocarbons and oxides.
In the event of a breakdown of the pollution sensor, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) turns off the automatic operation of the recirculation damper.
A/C compressor control (air conditioning)
A/C compressor (air conditioning) is a permanently installed capacity-controlled unit driven by a motor. Refrigerant flow through A/C compressor (air conditioning) , as well as the resulting system pressure and the operating temperature of the evaporator, are controlled by a solenoid valve in the refrigerant circuit. The solenoid valve in the refrigerant circuit is controlled by the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) using PWM signal (pulse width modulation) , modulated with a frequency of 400 Hz. PwM signal duty cycle (pulse width modulation) calculated using the following parameters:
- A/C Compressor Shaft Torque (air conditioning).
- Maximum Shaft Torque for A/C Compressor (air conditioning)
- A/C cooling system status (air conditioning).
- A/C system load (air conditioning).
- A/C refrigerant pressure (air conditioning).
- Outside temperature
- Fan speed
- Crankshaft scroll status
- Evaporator temperature.
- The current transmission gear.
If economy mode is selected, the PWM signal (pulse width modulation) keeps the solenoid valve in the refrigerant circuit in the position corresponding to the minimum allowable flow, thereby effectively turning off the A/C function (air conditioning).
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) sets the operating pressure limits in the refrigerant system. When the system pressure approaches the upper limit, the duty cycle of the PWM signal (pulse width modulation) gradually decreases until the pressure in the system begins to decrease. If the system pressure falls below the lower limit, the duty cycle of the PWM signal (pulse width modulation) maintained at a minimum level to ensure the minimum stroke of the A/C compressor (air conditioning), at which the amount of oil in the compressor of the A / C system (air conditioning) does not decrease. The protective algorithm allows you to quickly and at an early stage detect a sudden change in pressure associated with a malfunction in the system.
A/C Compressor Shaft Torque (air conditioning)
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) Calculates A/C compressor shaft torque based on refrigerant pressure, evaporator temperature and engine speed (air conditioning). The calculated value is transmitted via the medium speed CAN bus (controller LAN) to the ECM (engine control module) , which uses this value to control idle speed and air-fuel ratio. In addition, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) compares the calculated value with the maximum shaft torque of the A/C compressor (air conditioning), received from the ECM (engine control module) via medium-speed CAN bus (controller LAN). If the calculated value exceeds the maximum value, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) commands the solenoid valve in the refrigerant circuit to reduce the refrigerant flow to reduce the torque on the A/C compressor shaft (air conditioning) . By reducing the maximum shaft torque of the A/C compressor (air conditioning), ECM module (engine control module) can, if necessary, reduce the load on the engine in order to maintain the traction characteristics of the vehicle or prevent damage to the cooling system.
Idle control
To ensure the operation of the A/C system (air conditioning) , ATC controller (automatic temperature control) sends a request to increase the idle speed of the engine if the temperature in the evaporator has begun to rise, and the solenoid valve in the refrigerant circuit is already open, maintaining its maximum flow. The idle speed increase request message is sent in three stages over the medium speed CAN bus (controller LAN) to the ECM (engine control module) . For more information refer to Electronic Engine Controls (303-14A Electronic Engine Controls - 4.0L). For more information refer to Electronic Engine Controls (303-14B Electronic Engine Controls - 4.4L). For more information refer to Electronic Engine Controls (303-14C Electronic Engine Controls - 2.7L Diesel).
The grounds for changing the engine idle speed are defined as follows:
- If the evaporator temperature rises 3°or 6°above the set operating temperature within 10 seconds, the first request to raise the engine idle speed is sent.
- If the evaporator temperature rises 3°C or 12°C above the set operating temperature within 9 seconds after fulfilling the requirements of the first idle speed increase request, a second idle speed increase request is sent..
- If the evaporator temperature rises 3°C or 15°C above the set operating temperature within 10 seconds after fulfilling the requirements of the second idle speed increase request, a third idle speed increase request is sent..
- If the evaporator temperature drops by 3°within 10 seconds after fulfilling the requirements of the third request to increase the engine speed of the engine in idle mode, a request is sent to reduce the engine speed of the engine in idle mode.
Electrical load regulation
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) regulates the load of the onboard electrical system for the following purposes:
- Maintain sufficient charge in the vehicle battery.
- Provide adequate power to heat and defrost the windows while the engine is warming up.
- Provide proper power for the A/C system (air conditioning) for extended periods when the engine is idling.
- Maintain system voltage within acceptable limits.
- Provide proper power according to customers' requirements.
During engine warm-up, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) controls the electrical load to ensure that the battery voltage exceeds a preset level. This level, as well as the duration of the engine start, depend on the temperature of the outside air and the coolant. After the engine warms up, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) controls the electrical load, ensuring that the required electrical load does not exceed the capacity of the generator.
The duration of the engine warm-up period depends on the temperature of the outside air and coolant at the time the ignition is switched on (see table below):
Engine warm-up time
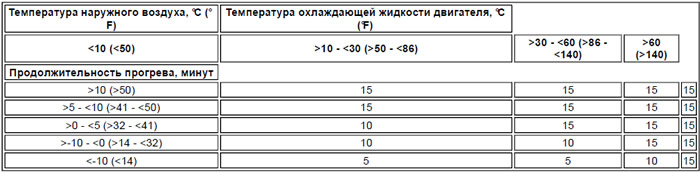
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) calculates the electrical load from devices connected to the battery and alternator and compares the result with the maximum allowable load on the alternator. The calculations determine the average value for the first 20 seconds after starting the engine, and then - the average values for every subsequent 60 seconds. After turning off the ignition, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) saves electrical load readings for 20 seconds. If the engine is restarted within 20 seconds, the ATC (automatic temperature control) module resumes electrical load management using the stored status. If the engine is restarted after 20 seconds, the timers are reset and the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) recalculates the state.
If the electrical load exceeds the maximum allowable value, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) sends a message with a request to increase the engine speed in idle mode on the medium speed CAN bus (controller LAN) on eCm module (engine control module) . If the excess electrical load persists after increasing the engine idle speed, or if the electrical load exceeds the capacity of the charging system, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) reduces the electrical load by reducing or turning off the power consumption of some on-board systems. The number of systems regulated in this way depends on how much the load needs to be reduced. These systems, and how to reduce or disable their power consumption, are listed in three tables. The use of one or another table depends on the temperature of the outside air, battery and engine coolant.
- The first table is used when starting the engine from a cold state at an air temperature of less than 5°C and a coolant temperature of less than 30°C.
- The second table is used when starting a warm engine at an air temperature of 5°C or more and a coolant temperature of less than 30°C.
- The third table is used when the battery temperature is 5°C or higher and the coolant temperature is over 50°C.
- If none of the above conditions are met, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) selects the table that was last used.
Electrical load control during cold start
| A priority | System | |
| Reduced energy consumption | Shutdown | |
| 1 | - | Air suspension |
| 2 | - | Front seat heaters |
| 3 | - | Infotainment system |
| - | 4 | Front seat heaters |
| 5 | - | Auxiliary climate control fan |
| 6 | - | Rear window heater |
| 7 | - | Heated mirrors and windshield washer nozzles |
| - | 8 | Heated mirrors and windshield washer nozzles |
| 9 | - | Windscreen heater |
| 10 | - | Main climate control fan |
| - | 11 | Auxiliary climate control fan |
| - | 12 | Rear window heater |
| - | 13 | Windscreen heater |
Controlling the electrical load when starting a warm engine
| A priority | System | |
| Reduced energy consumption | Shutdown | |
| - | 1 | Heated front seats, exterior mirrors and windshield washer nozzles |
| 2 | - | Windscreen heater |
| 3 | - | Rear window heater |
| 4 | - | Air suspension |
| 5 | - | Infotainment system |
| - | 6 | Windscreen heater |
| - | 7 | Rear window heater |
| 8 | - | Auxiliary climate control fan |
| - | 9 | Auxiliary climate control fan |
Continuous electrical load control
| A priority | System | |
| Reduced energy consumption | Shutdown | |
| - | 1 | Front seat heaters |
| 2 | - | Windscreen heater |
| 3 | - | Rear window heater |
| 4 | - | Auxiliary climate control fan |
| 5 | - | Air suspension |
| 6 | - | Infotainment system |
| - | 7 | Auxiliary climate control fan |
Changes in engine speed when idling and changes in the electrical load of systems that are not directly controlled by the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) (air suspension and infotainment system) carried out using messages transmitted over the medium-speed CAN bus (controller LAN) . If necessary, partial limitation of energy consumption
- The system continues to adjust the air suspension height, but the compressor capacity is limited because the reservoir is not filled.
- The Infotainment system continues to operate, but the maximum volume level is reduced and the frequency range of the output signal is reduced.
Cooling fan control
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) determines the energy required for cooling in the condenser based on the pressure of the refrigerant (there is a direct relationship between the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant). Cooling energy requirement reported to ECM (engine control module) via medium-speed CAN bus (controller LAN) . ECM module (engine control module) regulates the cooling of the condenser by means of a cooling fan. For more information refer to Electronic Engine Controls (303-14A Electronic Engine Controls - 4.0L). For more information refer to Electronic Engine Controls (303-14B Electronic Engine Controls - 4.4L). For more information refer to Electronic Engine Controls (303-14C Electronic Engine Controls - 2.7L Diesel).
Air temperature controllers
From the evaporator, the air enters the heater, where the temperature controller flaps direct part of the air through the heater core to obtain the desired air temperature at the outlet. In models with automatic systems, both temperature control dampers operate independently, allowing you to maintain different temperatures in the left and right sides. In models with manual control, the temperature controller dampers are driven by one stepper motor, and in automatic systems by two. One or two stepper motors are controlled by the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) using messages sent over the local LI N bus.
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) calculates the position of the stepper motor required to reach the set temperature and compares it with the current stored position. If these positions do not match, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) sends a command to the stepper motor to change position.
If the maximum cooling or maximum heating mode is selected, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) cancels all previous settings and sets the temperature, air source, fan speed and air distribution as shown in the following table.
NOTE: * If the engine is cold, a lockout may be activated that will stop the fan from running until the engine reaches operating temperature.
| Purpose | Maximum cooling | Maximum heating |
| Temperature control | Temperature control damper fully closed | Temperature control damper fully open |
| Air source | Recirculated air | Fresh air |
| Fan speed | Maximum | Maximum * |
| Air distribution | Face level air nozzle (with foot air function) | Nozzle for supplying air to the legs and to the windshield |
On models with automatic systems, setting the system to maximum heating or cooling in one of the zones may affect the temperature control in the second zone. In practice, maximum cooling or maximum heating can only be achieved if the temperature controls for the two interior zones are set to the same extreme positions.
In economy mode, the automatic temperature control function is still active, however, in the absence of cooling, the minimum outlet air temperature cannot be lower than the outdoor air temperature, and in practice it is even slightly higher due to the heating in the intake duct.
Air distribution controller
When the A/C system (air conditioning) works in automatic mode, ATC controller (automatic temperature control) automatically adjusts the air distribution in accordance with the established algorithm for creating comfortable conditions. Automatic control is canceled when manual modes are selected. The manual air distribution control is retained until the automatic mode is selected again. Temperature controller dampers are driven by two stepper motors controlled by the ATC controller (automatic temperature control), passing messages over the local LIN bus.
If both face and leg level air distribution is selected, when the air is heated, more of it is sent to the legs. If the air is cooled, most of it is removed at face level.
Fan control
If the A/C system is on (air conditioning) or manually set fan speed, ATC controller (automatic temperature control) energizes the fan coil in the BJB (battery junction box). The activated relay supplies battery power to the fan motor that is connected to "mass" through the fan control module. Fan speed controlled by PWM signal (pulse width modulation), which is supplied from the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) to the fan control module. The fan control module regulates the voltage on the fan motor according to the PWM signal (pulse width modulation).
In automatic fan mode, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) changes the fan speed in accordance with the algorithm for maintaining comfortable conditions. In manual fan mode ATC controller (automatic temperature control) sets one of seven fixed fan speeds selected on the control panel.
Programmed glass defrost
The function of programmed defrosting of car windows automatically allows you to perform this procedure with the greatest efficiency. If the programmed glass defrost function is selected, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) installs the following system configuration:
- Automatic operation is switched off.
- Outside air is supplied to the cabin, manual control.
- The previously selected temperature does not change, automatic control.
- Air is directed to the windshield, manual control.
- Fifth fan speed is set, manual control
- Rear and windshield heaters (if applicable) glasses included.
- A/C system (air conditioning) switches to automatic mode.
- Any air distribution switch is pressed. The reaction of the system will be identical to a normal change in air distribution with manual control.
- Pressing the auto mode switch. This press restores the fully automatic mode.
- Pressing the programmable defrost switch again. With this press, the system returns to the state that existed at the moment immediately before the first selection of the programmed defrost function.
- Switching off the ignition.
Air intake control
The system automatically selects the source of air intake, unless this mode is canceled when recirculation is manually turned on. In automatic control mode, ATC controller (automatic temperature control) determines the required position of the recirculation circuit damper in accordance with the algorithm for maintaining comfortable conditions and the input signal from the contamination sensor (if installed). The recirculation damper is driven by an electric motor controlled by wired analog signals from the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) . A potentiometer is installed on the electric motor, which returns to the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) position signal, providing automatic feedback control.
If recirculation has not been selected as the air intake source, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) adjusts the position of the damper of the recirculation circuit, reducing the air flow from the oncoming pressure when the car is moving.
After turning off the ignition, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) measures the outside air temperature. If the outside temperature is lower than the preset value, the recirculation mode is activated to prevent humid air from entering the passenger compartment during parking.
If the vehicle is in transport mode, each time the ignition is turned off, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) sets the damper on the air intake line to the recirculation position, regardless of the outside temperature.
Determination of air pollution
If the vehicle has a pollution sensor, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) selects the air intake source in such a way as to reduce the content of external pollutants in the intake air. This function is fully automatic but can be overridden by manually selecting the air source.
Humidity measurement
If a humidity sensor is installed, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) regulates the humidity in the car interior. An increase in the humidity of the air entering the passenger compartment is achieved by increasing the temperature of the evaporator, and a decrease in humidity is achieved by decreasing the temperature of the evaporator.
Front seat heaters
To switch on the heating of the front seats, turn the ignition switch to position II and select one of the two possible heating modes. The first time you press the front seat heater switch, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) sets the heating temperature to high, supplies power to the corresponding heating elements of the front seats. Two yellow LEDs on the switch light up (LEDs). When the switch is pressed a second time, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) sets a low heating temperature, and one of the LED (LEDs) goes out. When the switch is pressed a third time, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) turns off the heating, while the second LED goes out (LEDs) . The seat heaters remain on until they are turned off by the switch or until the ignition is turned off.
To the input of the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) it receives signals from the temperature sensors of both front seats, on the basis of which it regulates the power to the heating elements, controlling the temperature of the seats in the range between 35 and 45°C. The actual temperature settings depend on the type of seat upholstery as the different materials used have different thermal conductivity.
If the front seat heaters are turned on in high temperature mode, after a certain time, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) automatically switches them to low temperature mode. The time before switching depends on the air temperature in the passenger compartment.
Time to switch to low temperature mode
| Temperature in the cabin,°С (° F) | <-15 (5) | -15-10 | -10-0 | 0 -15 | 15-25 | >25 (77) |
| Delay, minutes | Remains in high temperature mode until manual override | 20 | 15 | 10 | 5 | 3 |
To protect the heating elements, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) turns off the heated front seats if the battery voltage exceeds 16.5±0.3 V for 5 seconds or more. After the battery voltage drops to 16.2±0.3 V, the front seat heating is switched on again.
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) regulates the power supply to the heating elements and, if a short circuit or open circuit is detected, turns off the heating of the corresponding front seat. In addition, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) turns off the seat heating when the set seat temperature is too high.
Also ATC controller (automatic temperature control) monitors the reliability of signals coming from temperature sensors. If, when the seat heating is on, the signal from one of the temperature sensors shows that the actual temperature is no more than 5°C (9°F) below setpoint, ATC controller (automatic temperature control) monitors the temperature increase on a signal from this sensor and checks that the temperature does not go beyond the maximum or minimum allowable value. If the sensor indicates that the temperature is close to the upper limit of the operating range when the outside air temperature and the engine temperature coincide within 10°C (18°F), ATC controller (automatic temperature control) turns off the heated front seats until the sensor signal indicates that the temperature has dropped to a preset value. aTC controller (automatic temperature control) interprets a temperature sensor signal of -45°C or lower as an open circuit, and a signal of 100°C or more as a short circuit.
Rear window heater
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) controls the operation of the rear window defroster, directing via the medium-speed CAN bus (controller LAN) messages that control the rear defroster relay located in the CJB (central distribution block) . CJB unit control module (central switching unit) interprets messages coming from the CAN bus (controller LAN) , and switches connections from "weight" winding of the relay that controls the operation of the rear window heater. When the rear window defroster relay is activated, battery power is supplied to the rear window heaters. Heated rear window only works when the engine is running.
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) turns on the rear window defroster with certain cycles, changing the power and duration of heating. The characteristics of the heating cycle depend on the outside temperature and whether it is the first or next heating operation in the current ignition cycle.
When the heater switch is pressed, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) activates the corresponding heating cycle, while the LED on the switch lights up (LEDs) . LED () stays on until the rear defroster is turned off, another heating cycle is completed, or the engine is stopped. If the engine is restarted within 20 seconds after the engine is stopped or the ignition is turned off, the heated rear window will resume.
After turning on the rear window defroster for the first time, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) sets a short or long time interval with maximum defrost power, after which it switches to reduced power mode. The defrost mode used depends on the outdoor temperature. In the reduced power phase, the relay switches off the rear window defroster after 80 seconds of operation and switches it on again after 40 seconds.
On subsequent power-ups in the current ignition cycle, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) for a fixed time turns on the rear window defroster at maximum power.
Heated rear window phases
| Phase | Time, minutes |
| Short defrost cycle (-5°С and above) | 10 |
| Long defrost cycle (below -5°С) | 15 |
| Reduced power | 20 |
| Subsequent switching on of the heater | 10 |
Windscreen heater
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) controls the operation of the defroster windshield using the defroster relay installed in the BJB (battery mounting box). For this ATC controller (automatic temperature control) switches connections from "weight" winding of the relay that controls the operation of the windshield defroster. After the relay is turned on, battery power begins to flow to the two heating elements of the windshield defroster. The windshield is heated only when the engine is running.
ATC controller (automatic temperature control) turns on the windshield defroster with certain cycles, changing the power and duration of heating. The characteristics of the heating cycle depend on the outside temperature and whether it is the first or next heating operation in the current ignition cycle.
When the defroster switch is pressed, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) activates the corresponding heating cycle, while the LED on the switch lights up (LEDs). LED () stays on until the windshield defroster is turned off, another heating cycle is completed, or the engine is stopped. If the engine is restarted within 20 seconds after the engine has been stopped or the ignition switched off, the heated windshield will resume.
When the windshield defroster is turned on for the first time, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) sets a short or long time interval with maximum heating power, after which it switches to reduced power mode. The defrost mode used depends on the outdoor temperature. In the reduced power phase, the relay switches off the heated windshield after 80 seconds of operation and switches it on again after 40 seconds.
On subsequent power-ups in the current ignition cycle, the ATC controller (automatic temperature control) turns on the windshield defroster at maximum power for a fixed time.
Phases of inclusion of a defroster of a windshield
| Phase | Time, minutes |
| Short defrost cycle (-5°С and above) | 3 |
| Long defrost cycle (below -5°С) | 5 |
| Reduced power | 10 |
| Subsequent switching on of the heater | 3 |
Control scheme of the manual control system
NOTE: A = wired connections; D = high speed CAN bus (controller LAN); N = Medium speed CAN bus (controller LAN); O = LIN bus
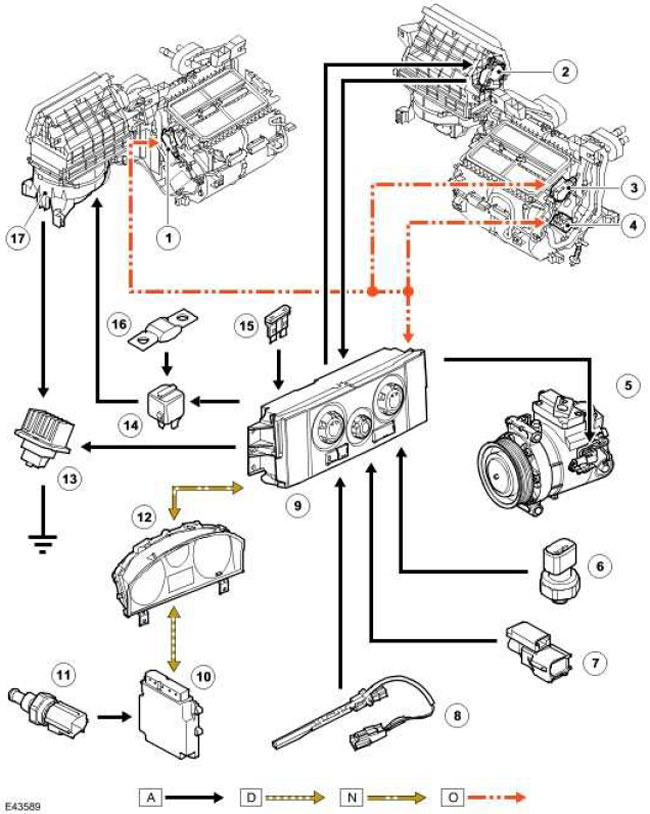
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | Damper motor for air distribution to the face and feet | |
| 2 | Recirculation damper motor | |
| 3 | Windscreen damper motor | |
| 4 | Temperature damper motor | |
| 5 | A/C Compressor Solenoid Valve (air conditioning) | |
| 6 | Refrigerant pressure sensor | |
| 7 | Outdoor temperature sensor | |
| 8 | Evaporator temperature sensor | |
| 9 | ATC module (automatic temperature control) | |
| 10 | ECM (engine control module) | |
| 11 | ECT sensor (engine coolant temperature) | |
| 12 | Dashboard. | |
| 13 | Fan control module | |
| 14 | Fan Motor Relay | |
| 15 | Fuse 51P, in CJB (central switching unit) (continuous battery power) | |
| 16 | Fuse link 12E, in BJB block (battery mounting box) | |
| 17 | blower fan |
Automatic system control scheme
NOTE: A = wired connections; D = high speed CAN bus (controller LAN); N = Medium speed CAN bus (controller LAN); O = LIN bus
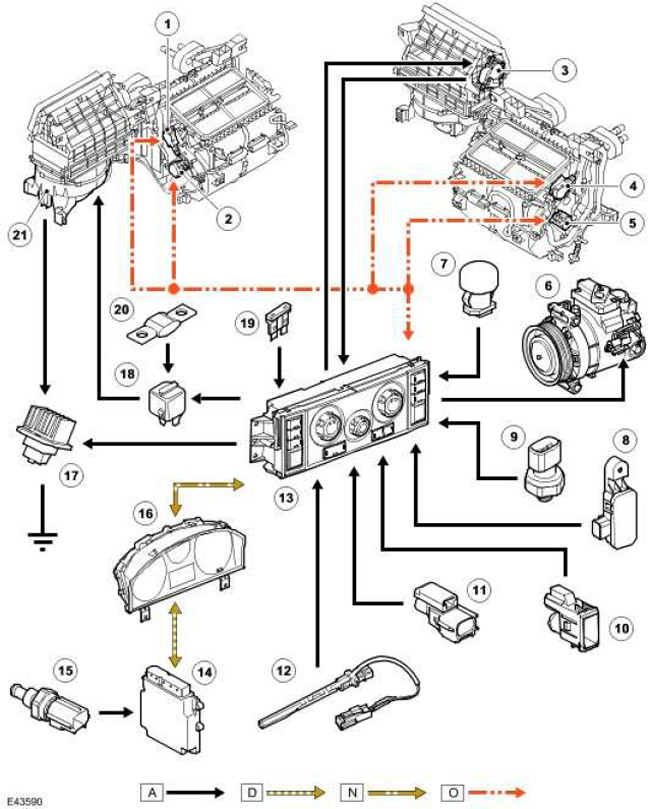
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | Electric damper motor for air distribution in the face and in the legs | |
| 2 | LH (left) temperature controller damper motor | |
| 3 | Recirculation damper motor | |
| 4 | Windshield damper motor | |
| 5 | RH (right) temperature controller damper motor | |
| 6 | A/C Compressor Solenoid Valve (air conditioning) | |
| 7 | Solar radiation sensor | |
| 8 | Dirt sensor (Japan only) | |
| 9 | Refrigerant pressure sensor | |
| 10 | Cabin air temperature sensor (all models with an automatic system, except those intended for Japan); interior temperature and humidity sensor (Japan-only models with automatic system) | |
| 11 | Outdoor temperature sensor | |
| 12 | Evaporator temperature sensor | |
| 13 | ATC module (automatic temperature control) | |
| 14 | ECM (engine control module) | |
| 15 | ECT sensor (coolant temperature) | |
| 16 | Dashboard | |
| 17 | Fan control module | |
| 18 | Fan Motor Relay | |
| 19 | Fuse 51P, CJB (central switching unit) (continuous battery power) | |
| 20 | Fuse link 12E, in BJB block (battery mounting box) | |
| 21 | blower fan |
Comments on this article