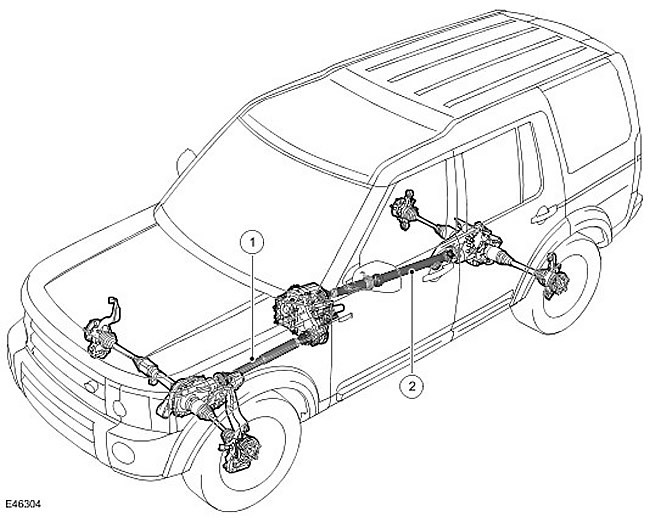
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | Front drive shaft |
| 2 | - | Rear drive shaft |
General information
Drive shafts are used to transmit torque from the transfer case to the front and rear differentials.
The front drive shaft is a single piece that connects the transfer case to the front differential via constant velocity joints (SHRUS).
The rear drive shaft is in two parts and, due to the increased length, is supported by a central bearing. The rear drive shaft is connected to the transfer case via a CV joint, and to the rear differential via a cardan joint. These hinges allow angular deviations of the drive shaft during acceleration and deceleration.
The front and rear driveshafts are maintenance free and the entire driveshaft assembly will need to be replaced in the event of a failure.
Front drive shaft
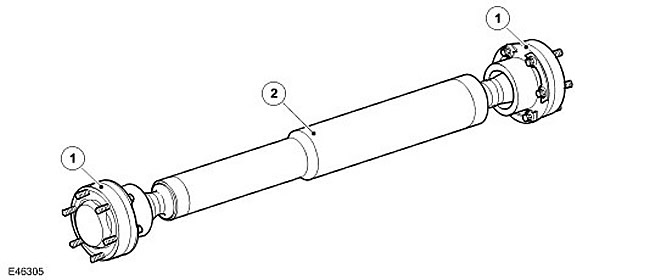
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | SHRUS |
| 2 | - | Front drive shaft |
The front drive shaft is made of steel pipe with a wall thickness of 1.7 mm. CV joint is fixed on each side of the drive shaft (for more information about CV joints, see section "axle joint"). The nominal total shaft length is 713 mm.
Each CV joint has 6 holes for attaching to the front differential's primary flange and the transfer case's front output flange. The CV joints are attached to the front differential and transfer case with 6 Torx bolts, seated on a sealant.
Compression washers are installed under each pair of bolts. These washers are necessary to prevent compression of the CV joint mounting flange.
A protective cover is pressed onto the CV joint. The tightness of the connection of the cover with the hinge body is provided by an internal gasket, and with the front output flange of the transfer case - by an end cap and an internal gasket. This prevents dirt and moisture from getting inside. The CV joint allows movement of the drive shaft caused by small movements in the gearbox and transfer case bearings.
Rear drive shaft assembly
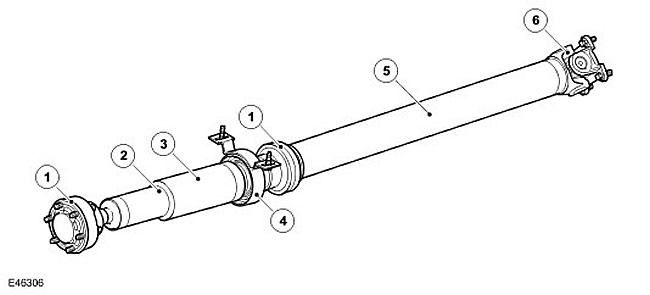
| Item name | Spare part number | Description |
| 1 | - | SHRUS |
| 2 | - | Deformable section |
| 3 | - | Front shaft assembly |
| 4 | - | Thrust bearing |
| 5 | - | Rear shaft assembly |
| 6 | - | Cardan joint |
The rear drive shaft assembly consists of the front and rear shaft assemblies and a centrally located thrust bearing. The nominal overall length of the rear drive shaft assembly is 1309 mm.
Front shaft assembly
The front shaft assembly has a deformable tube element that adjusts "folding" drive shaft in an accident.
A CV joint is installed on each side of the front shaft assembly (for more information about CV joints, see section "axle joint").
Front CV joint (from the transfer box) has 6 radial holes for attaching to the rear output flange of the transfer case. The CV joint is attached to the outlet flange with 6 Torx bolts screwed into the threaded holes in the flange. Compression washers are installed under each pair of bolts. The rear splined shaft is engaged with the rear shaft CV joint hub, pressed in and secured with Locktite. A support bearing is installed on the machined surface of the shaft by a press fit.
Rear shaft assembly
The rear shaft assembly has a rear (from the rear differential) Hooks type cardan joint.
The universal joint is welded to the rear shaft tube and attached to the rear differential input shaft with 4 flange nuts. The opposite end of the rear shaft pipe is welded directly to the CV joint housing.
Thrust bearing assembly
The support bearing assembly consists of a pressed steel housing, a rubber diaphragm and a ball bearing. The diaphragm is fixed in the body. An inner metal ring mounted on the bushing allows the bearing to be pressed in. The rubber bushing allows minor axle misalignments and also serves to dampen vibrations. The thrust bearing assembly is secured with screws that pass through non-threaded holes in the bearing assembly and thread into nuts welded on the inside of the chassis cross member.
Cardan joints
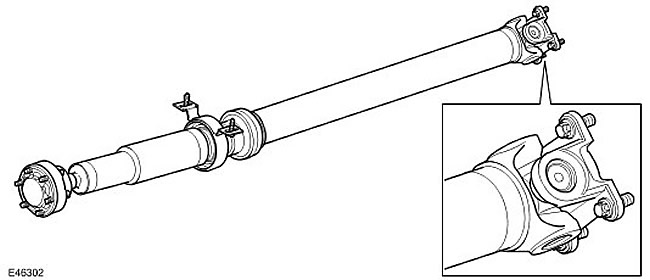
A Hookes type universal joint is used to connect the rear driveshaft assembly to the rear differential, allowing the driveshaft to be angularly deflected during acceleration and deceleration.
The hinge is attached to the input shaft of the rear differential with 4 screws with flanges seated on the sealant. During manufacture, the hinge is lubricated and sealed for life.
Comments on this article