- Cylinder block
- Piston cooling nozzles
- Rear oil seal and crankshaft holder
- Connecting rods and pistons
- crankshaft position sensor (CKP)
- Starter
- Generator
- Coolant pump and vacuum pump
- Power steering pump
- High pressure fuel pump
- Coolant Distribution Manifold
Cylinder block
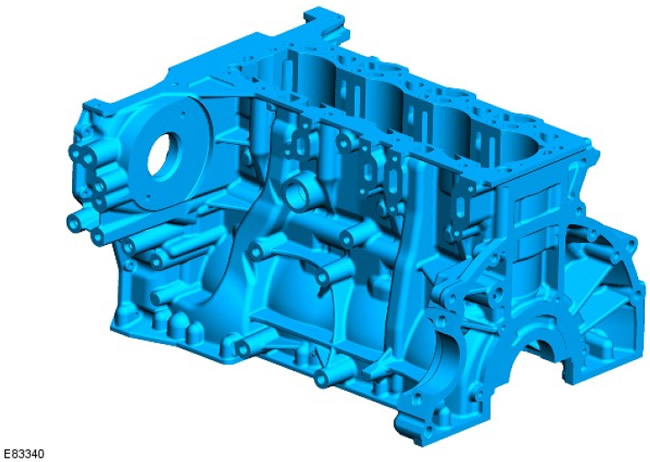
The cylinders and crankcase are located in the cylinder block, which is a hollow monobloc structure made of gray cast iron. This design requires less material than a traditional cast iron engine block, reducing engine weight and length.
The cylinders are bored directly into the cylinder block.
Three different cylinder diameters are used in the manufacture of automobiles. This allows you to very accurately adjust the clearances between the pistons and cylinders.
The filter on the inlet oil line of the turbocharger is mounted on neck 1; it prevents foreign particles from the engine from entering the turbocharger and damaging the bearings.
Piston cooling nozzles
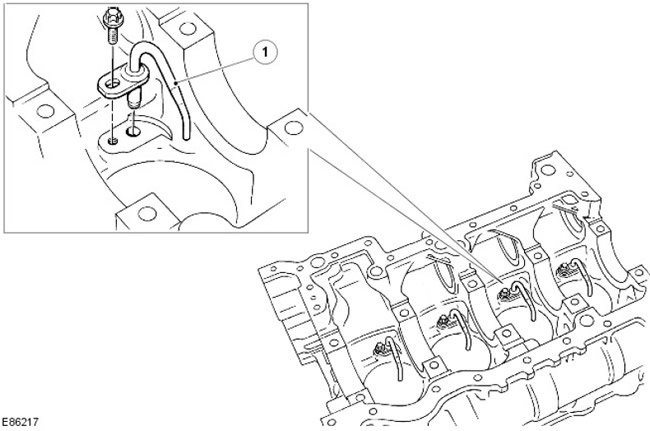
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Piston cooling nozzle |
A nozzle located in the cylinder block provides lubrication and cooling of the piston and piston pin. These nozzles spray oil into the piston, after which the oil, flowing through the internal undulating channel, helps to cool the piston head.
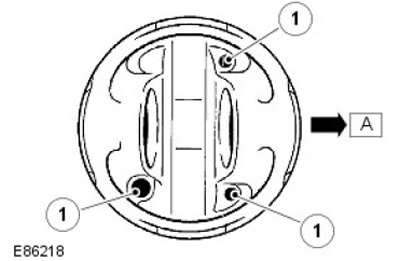
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| A | - | Front of the engine |
| 1 | - | Channels of the oil cooling system |
Oil flows through the main oil line and channels in the cylinder block to all major moving parts of the engine. Oil flows to the crankshaft main bearings, and through the shaft drillings to the connecting rod bearings.
Connecting rods and pistons
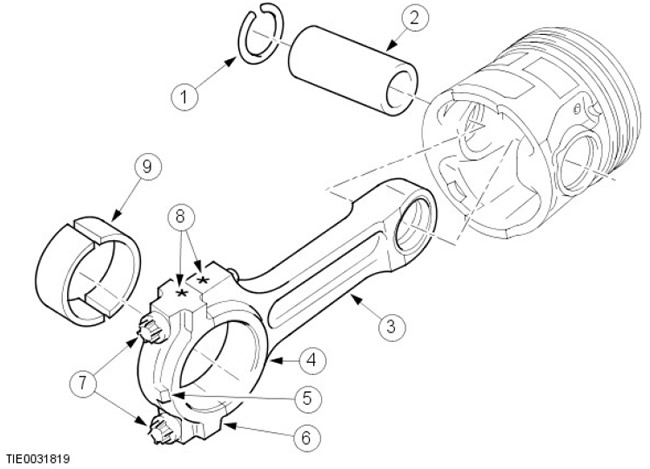
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Retaining ring |
| 2 | - | piston pin |
| 3 | - | connecting rods |
| 4 | - | Connecting rod bearing shell |
| 5 | - | ledge |
| 6 | - | bearing cap |
| 7 | - | bolts |
| 8 | - | Identification |
| 9 | - | bearing shell |
The rods are made from high strength steel. Selectively selected aluminum-tin split plain bearings are used as connecting rod bearings. The connecting rod bearing has a special coating that allows the bearing to withstand heavy loads and increases its service life.
There are 3 different crank length options. For identification purposes, the connecting rod and bearing cap are marked with an appropriate identification code.
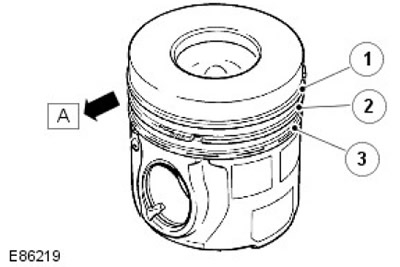
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| A | - | Front of the engine |
| 1 | - | Top compression ring |
| 2 | - | Lower compression ring |
| 3 | - | Oil scraper ring |
The pistons are made of aluminum alloy and equipped with three rings. The intake air flow swirls in the combustion chamber. The turbulent motion promotes the formation of an air-fuel mixture and its complete combustion. In addition, oil grooves are machined into the piston head to improve cooling (for more information, see the section on piston cooling nozzles).
When installing the pistons, make sure that all arrows on the piston heads point towards the front of the engine.
Each piston is mounted on a piston pin mounted in an aluminium-tin bushing in the connecting rod.
Rear oil seal holder
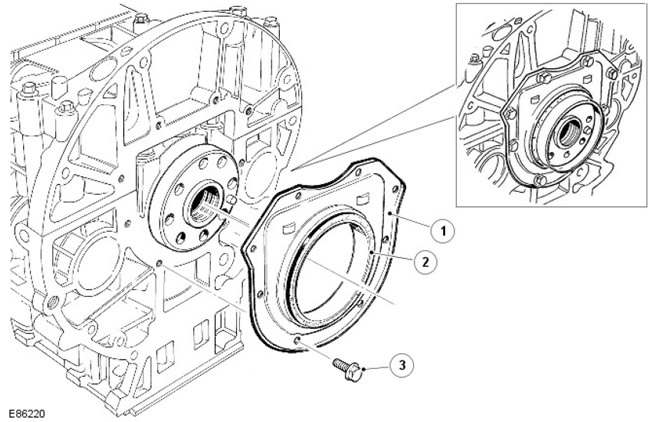
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Rear oil seal |
| 2 | - | Rear oil seal |
| 3 | - | Bolt (8 pcs.) |
The crankshaft rear oil seal holder is attached to the rear of the cylinder block with 8 bolts through a rubber seal.
Crankshaft position sensor (CKP)
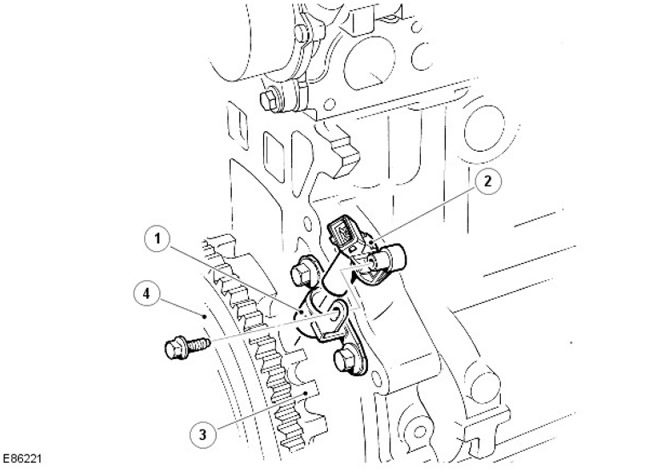
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Mounting bracket CKP |
| 2 | - | CKP sensor (angle of rotation of the crankshaft) |
| 3 | - | Pulse (defining) wheel |
| 4 | - | Flywheel |
The CKP sensor is located on the flange of the cylinder block and gearbox. The sensor generates an input signal of the speed and position of the crankshaft. The sensor uses the Hall effect, based on which the sensor monitors the rotation of the impulse wheel on the back of the crankshaft. If the CKP sensor bracket has been removed, it must be properly aligned during installation.
For more information, see the chapter: Electronic controls (303-14 Electronic Controls - Diesel Engine ID4 2.4L, Description and Operation).
Starter
The starter is mounted at the rear left of the cylinder block, on the gearbox flange.
For more information, see the chapter: Starting system (303-06 Starting system - Diesel engine ID4 2.4L, Description and principle of operation).
Generator
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Alternator Support Bracket |
| 2 | - | Generator |
The alternator is mounted on the right side of the engine on a mounting bracket that is bolted to the cylinder block. The accessory drive belt is used to drive the alternator from the crankshaft pulley.
For more information, please refer to the chapter: Generator - ID4 2.4L Diesel Engine (414-02 Generator and voltage regulator - Diesel engine ID4 2.4L, Description and principle of operation).
Coolant pump and vacuum pump
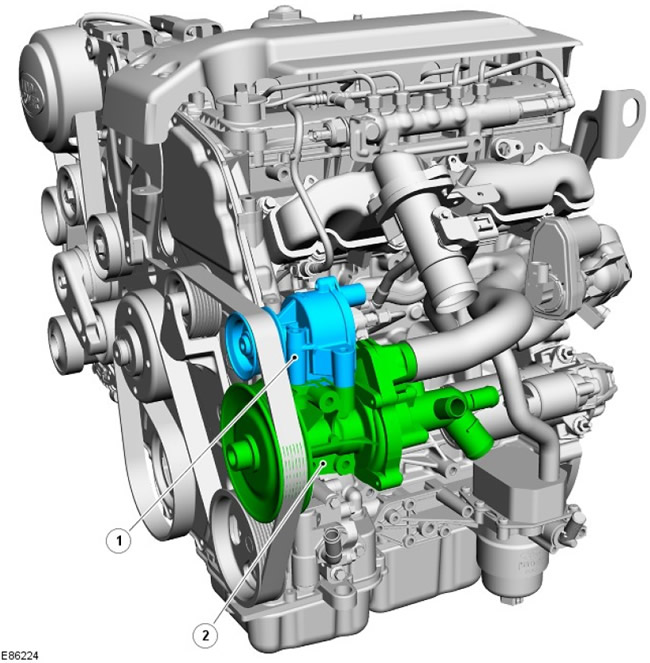
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Vacuum pump |
| 2 | - | coolant pump |
The coolant pump is mounted on the left front of the cylinder block and secured with 4 bolts. The coolant pump is driven by the crankshaft through the accessory drive belt. The engine thermostat is located at the rear of the coolant pump housing; thermostat opens at 88°C.
For more information, see chapter: Engine Cooling (303-03 Engine Cooling -ID4 2.4L Diesel Engine, Description and Function).
The vacuum pump is mounted on the coolant pump and secured with 3 bolts. The vacuum pump is also driven by the crankshaft via the accessory drive belt.
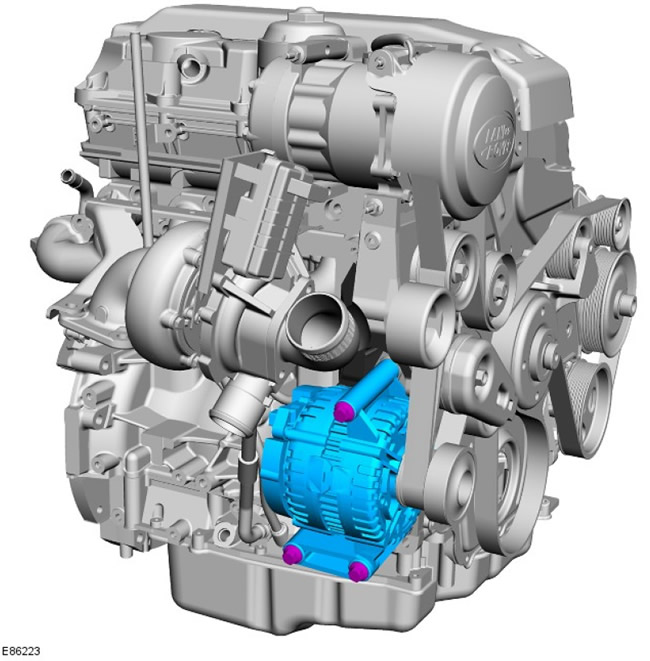
Power steering pump
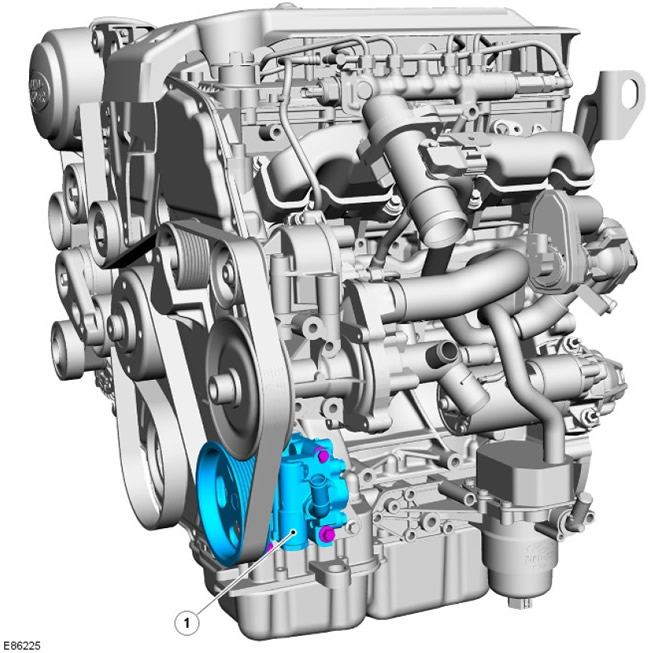
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Power steering pump |
The power steering pump is located at the front left of the cylinder block, directly below the coolant pump. The power steering pump is attached to the mounting bracket with 3 bolts; The mounting bracket is fixed to the cylinder block and ladder frame with 4 bolts.
For more information, see the chapter: Power Steering (211-02 Power steering, description and principle of operation).
High pressure fuel pump
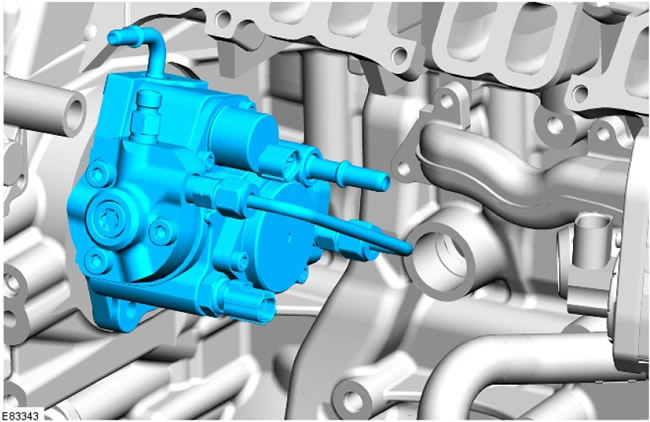
The injection pump is located under the intake manifold behind the water pump/vacuum pump assembly. The fuel pump is driven by a timing chain located at the front of the engine and includes a low pressure pump and a high pressure pump that function as a single unit.
The pump serves as a transitional element between the low and high pressure circuits. Its purpose is to supply fuel at the required pressure under all operating conditions throughout the life of the vehicle.
The transfer pump draws fuel from the fuel tank and forces it through the fuel filter. It then supplies fuel to the high pressure pump. The transfer pump maintains a constant fuel pressure through a control valve built into the fuel pump. This pressure is called transfer pressure.
The high pressure pump receives fuel at transfer pressure from the transfer pump and increases the fuel pressure. The high pressure fuel is then transferred from the injection pump to the common rail system.
For more information, see the chapter: Fuel supply and controls (303-04A Fuel supply and controls - ID4 2.4L diesel engine, Description and operation).
Coolant Distribution Manifold
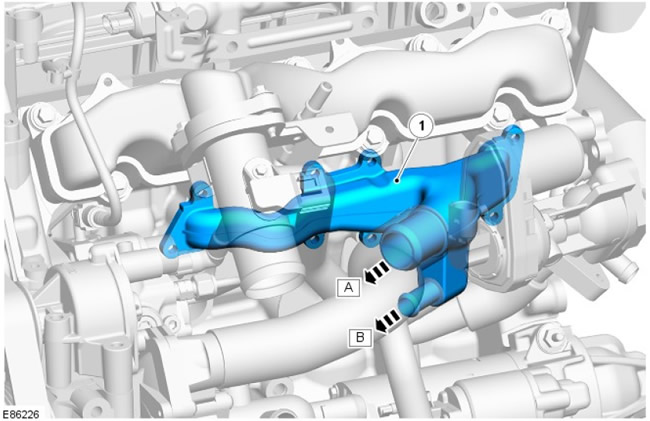
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| A | - | Coolant pump connection |
| B | - | Oil cooler connection |
| 1 | - | Coolant Distribution Manifold |
The coolant distribution manifold is located on the left side of the cylinder block under the intake manifold. The manifold receives coolant from the cooling system pump, which is then distributed to the cylinder block and to the engine oil cooler.
Comments on this article