Review
The operation of the clutch system is based on the well-known principle of hydraulically driving a single driven disc and clutch housing diaphragm spring assembly from the clutch pedal. When the clutch pedal is depressed, hydraulic fluid is pumped through the master cylinder, piping system and co-axial slave cylinder and eventually drives the clutch fingers to disengage the clutch and disengage the actuator and crankshaft. When the foot is removed from the pedal, the spring presses the pressure plate against the driven plate, which, in turn, is pressed against the flywheel. As a result, the crankshaft of the engine engages with the input shaft of the gearbox, forcing them to rotate at the same speed.
The clutch system has a conventional design and includes the following main components:
- Clutch master cylinder and pressure pipes
- Co-Axial Slave Cylinder Assembly Outlet and Torque Limiter
- Vibration damper (only for left-hand drive vehicles)
- Coaxial slave cylinder
- Clutch cover assy
- Driven clutch disc
- Flywheel
Clutch Master Cylinder
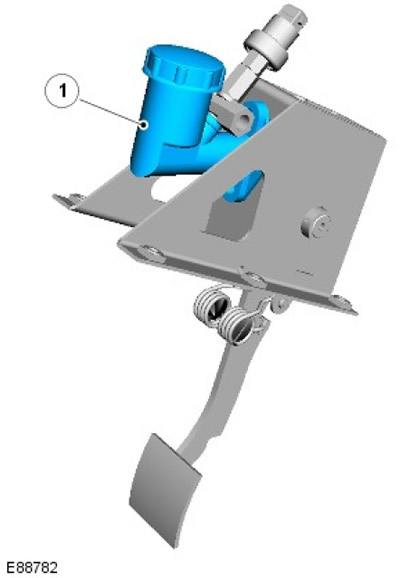
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Clutch Master Cylinder |
The clutch master cylinder is attached directly to the pedal box assembly located in the footwell on the driver's side.
The cylinder contains a piston assembly with a rod connected to the clutch pedal and spring. When depressed, the clutch pedal pushes the piston through the linkage. Pressing the pedal further increases the pressure in the cylinder and pipelines.
The cylinder has two hydraulic connections:
- With low pressure supply tube (through which fluid is supplied from the brake fluid reservoir)
- With high pressure tube
Pedal travel is limited by an upper stop built into the master cylinder and a lower stop built into the pedal mounting block.
Release of the coaxial working cylinder assy
NOTE: The illustration shows a right hand drive vehicle.
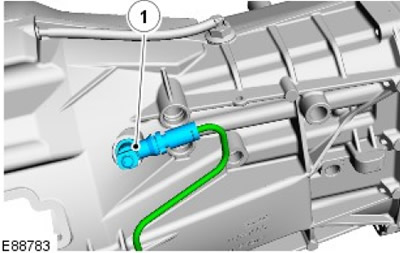
| Pos. | spare part no | Name |
| 1 | - | Assembly slave cylinder outlet and torque limiter |
The outlet of the co-axial slave cylinder assembly connects the external piping to the clutch release system built into the clutch housing. The mounting bracket ensures proper orientation of the assembly. A seal is provided between the assembly and the clutch housing.
Inside the slave cylinder release assembly is a maximum torque limiter. This element is designed to restrict the flow of hydraulic fluid during the upstroke of the clutch pedal. When the pedal is depressed normally, this limitation is imperceptible, however, in the event of an inadvertent release of the pedal (e.g. when a wet boot slips off the clutch pedal) Peak torque limits the rate of return flow and protects the gearbox and transmission from excessive shock loads that can cause damage.
On left-hand drive vehicles, the hydraulic piping system contains an anti-vibration damper inserted into the peak torque limiter socket. This is to reduce pedal noise or vibration during clutch operation.
Coaxial slave cylinder
The coaxial slave cylinder assembly consists of a clutch release bearing and a hydraulic slave cylinder. The entire assembly is attached to the front of the gearbox with 3 bolts. The bolts are arranged asymmetrically, which ensures the required angular position of the working cylinder, which, moreover, is centered by a collar. In the free state, the slave cylinder is fully extended, and after installing the clutch housing on the engine, it automatically assumes the correct position. The node does not need any tuning or adjustment.
Clutch cover assy
Clutch cover assembly includes pressure plate, cover and diaphragm. It is mounted on the flywheel and rotates with it.
The surface of the pressure plate has been machined to ensure tighter contact with the driven plate. The protrusions along the outer diameter of the pressure plate with the help of leaf springs connect it to the casing. The leaf springs are equipped with sheets that help to move the pressure plate away from the drive plate when pressing the clutch pedal.
The casing contains all the elements of the pressure plate. Flanged rivets support the diaphragm inside the cap. The rivet heads are beveled to allow the diaphragm to rotate when pressure is applied to it from the clutch release bearing. Holes in the housing are located on the pins on the flywheel, and additional holes provide fastening of the housing to the flywheel. Enlarged openings in the casing provide ventilation for the contact surfaces of the driven disc, pressure plate and flywheel.
The diaphragm contains a cast ring with petals. The diaphragm is attached to the housing with collared rivets. The inner head of each rivet is beveled to allow the diaphragm to rotate when the clutch is engaged or disengaged. When force is applied to the diaphragm petals from the clutch release bearing, the diaphragm pivots on its rivets and moves away from the pressure plate, relieving force from the pressure plate and allowing the driven plate to slide between the pressure plate and flywheel.
Driven clutch disc
The clutch disc is located between the flywheel and the clutch cover assembly pressure plate. The clutch disc has a splined hub that engages with the splines on the gearbox input shaft. The splined hub is located on an inner plate containing three pre-damping compression springs. The inner plate is held by springs capable of compressing in both directions to dampen engine vibration when idling. The inner plate rests on four even larger compression springs, which in turn rest on the central plate. The hub is located between the center plate and the friction damper. The friction damper includes spring rings that are located between the hub and the center plate. Spring rings reduce transmission noise and vibration associated with engine cycling.
Flywheel
The single flywheel is bolted to a flange on the engine crankshaft. The correct location of the flywheel is ensured by a pin. The ring gear is located on the outer diameter of the flywheel and is located opposite the flange. The ring gear is permanently mounted on the flywheel and is a serviceable element that can be replaced in case of damage or wear.
In order to provide a smooth surface for engaging the clutch disc, the working surface of the flywheel is machined.
Tightening torques
| Description | Nm | lb-ft |
| Clutch pressure plate bolts (need to install new bolts) | 29 | 21 |
| Clutch Slave Cylinder Bolts | 10 | 7 |
| Bolts of fastening of the main cylinder of coupling to the pedal block | 23 | 17 |
| Bolts of fastening of the pedal block of coupling to a partition of a motor compartment | 23 | 17 |
| Clutch Master Cylinder Rod Nuts | 23 | 17 |
Comments on this article